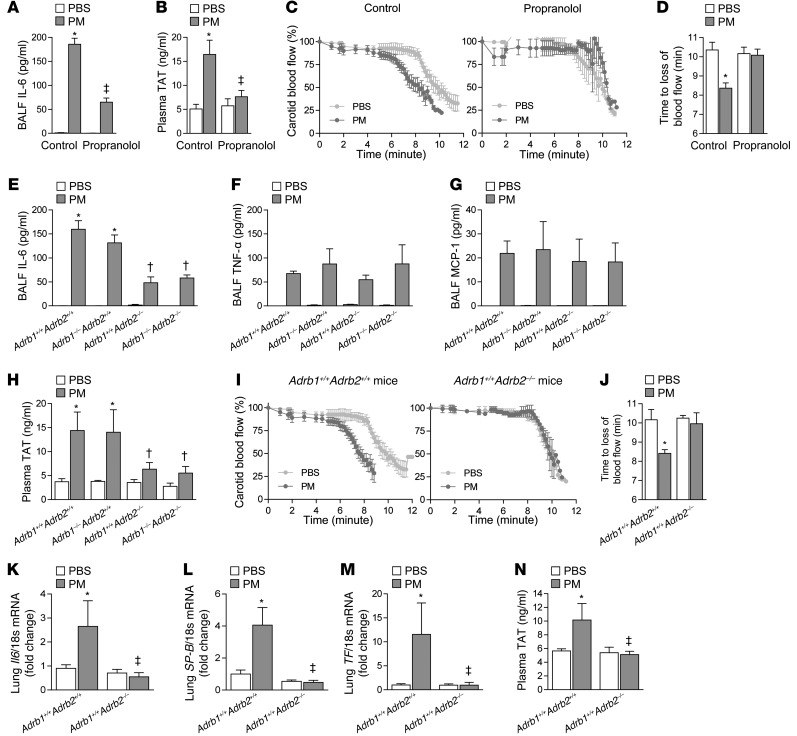
Figure 2. β2ARs are required for the catecholamine-induced upregulation of IL-6 and the resulting thrombosis after PM exposure.
We pretreated mice with propranolol (3 mg/kg in 100 μl i.p.) or vehicle (saline 100 μl i.p.) every 8 hours, followed 24 hours later by PM (200 μg/mouse) or control (PBS) and measured (A) the levels of IL-6 in the BALF, (B) the plasma levels of TAT complexes, and (C) the time to loss of blood flow after FeCl3-induced injury to the carotid artery. (D) The time to complete (>75% reduction) loss of blood flow is shown. We performed intratracheal instillations in mice lacking either β1AR (Adrb1–/–Adrb2+/+), β2AR (Adrb1+/+Adrb2–/–), or both β1AR and β2AR (Adrb1–/–Adrb2–/–) and their wild-type littermate controls (Adrb1+/+Adrb2+/+) with PM or PBS and, 24 hours later, measured the levels of (E) IL-6, (F) TNF-α, and (G) MCP-1 in BALF, (H) the plasma levels of TAT complexes in the plasma, and (I and J) the time to loss of blood flow after FeCl3-induced injury to the carotid artery. We exposed β2AR deficient mice (Adrb1+/+Adrb2–/–) and wild-type littermate controls (Adrb1+/+Adrb2+/+) contemporaneously to either CAPs (PM2.5) or filtered air for 8 hours daily on 3 consecutive days and measured levels of (K) Il6, (L) SP-B, and (M) TF mRNA in the lung tissue and (N) TAT complexes in the plasma. *P < 0.05, PM vs. PBS or CAPs vs. FA; ‡P < 0.05, propranolol vs. control, Adrb1+/+Adrb2–/– and Adrb1–/–Adrb2–/– vs. Adrb1–/–Adrb2+/+ and Adrb1+/+Adrb2+/+.