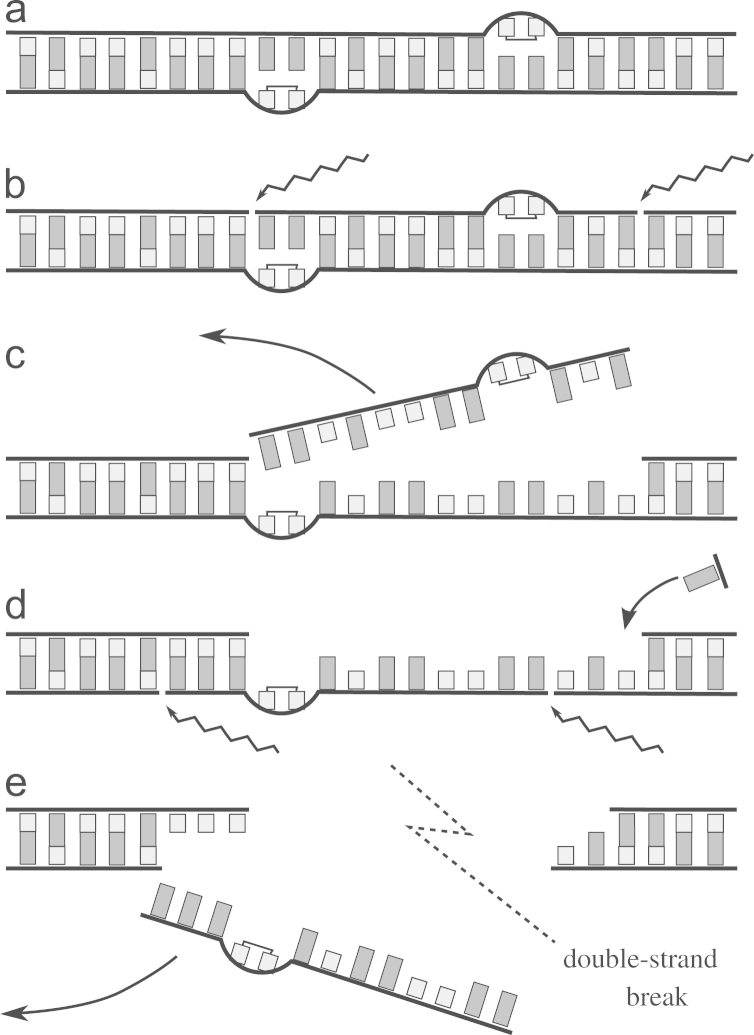
Fig. 1.
Double-strand break caused by repair of two close damage lesions. (a) A DNA molecule with two close damage sites lying on opposite strands. Repair is initiated on one of the strands, first by cutting the DNA backbone around the damage (b), followed by excision of the DNA segment with the damage (c). The excised region starts to be reconstructed using the other strand as a template (d). However, if a new repair starts in the other damaged site before the gap created by the first repair has been closed (d), a portion of the DNA molecule loses both strands and the molecule is broken into two, creating a double-strand break (e).