Figure 3.
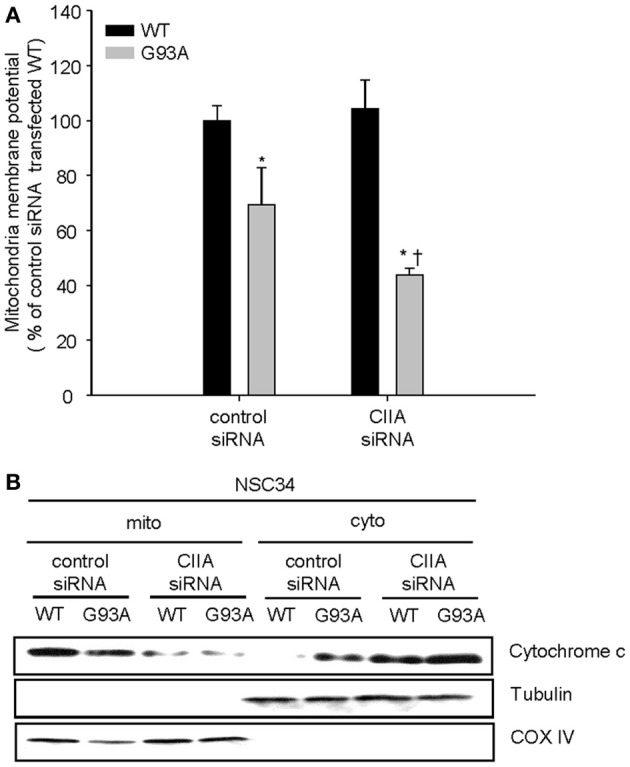
CIIA inhibits SOD1(G93A)-induced reduction of mitochondria membrane potential (Δψm) and the release of cytochrome c. NSC34 cells were stably transfected with plasmid vectors encoding Flag-tagged SOD1(WT) or SOD1(G93A) along with vectors for GFP or CIIA siRNA. (A) mitochondria membrane potential (Δψm) was analyzed by measuring the fluorescence intensity of tetramethyl rhodamine methyl ester (TMRM, a mitochondria potential sensor). Quantitative data are mean ± s.e.m. from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. WT; †P < 0.05 vs. G93A. (B) Cell lysates were subjected to the subcellular fractionation to obtain the mitochondrial (mito) and the cytosolic (cyto) fractions. Each fraction was subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies to cytochrome c, to α-tubulin (cytosolic marker), or to COX IV (mitochondrial marker).
