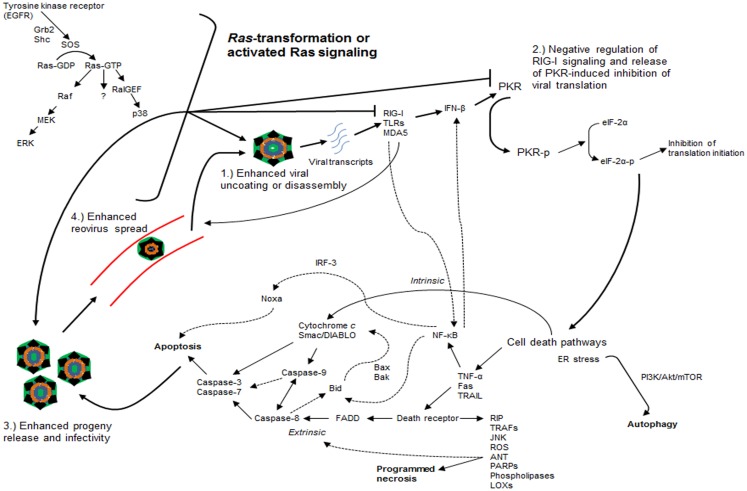
Figure 2.
Ras-transformation affects several steps of the reovirus infectious cycle to promote oncolysis. Ras-transformation affects multiple steps of the infectious life cycle in promoting reovirus oncolysis by: (1) enhancing virus uncoating and disassembly, (2) negative regulation of retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) signaling and releasing dsRNA-activated protein kinase (PKR)-induced translational inhibition, (3) increasing progeny release through enhanced apoptosis and generating more infectious progeny, and (4) enhancing viral spread in subsequent rounds of infection. Reovirus-induced cancer cell death occurs through autophagic, apoptotic, and necrotic pathways. Programed necrosis or necroptosis occurs through binding of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), Fas ligand (Fas), and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) to death receptors leading to downstream signaling involving receptor interaction protein kinase (RIP) 1 and 3, cylindromatosis (CYLD), TNF receptor-associated factors (TRAFs), stress-activated c-Jun NH2-terminal protein kinase (JNK), reactive oxygen species (ROS), adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT), poly ADP-ribose polymerases (PARPs), phospholipases, and lipoxygenases (LOXs). Apoptosis occurs through both extrinsic [e.g., TRAIL binding to cell surface death receptor recruits Fas-associated death domain (FADD), which recruits and activates the initiator caspase-8 that ultimately activates effector caspases-3 and -7] and intrinsic pathways [cytochrome c and second mitochondrion-derived activator of caspase (Smac/DIABLO) release with activation of downstream effector caspases with or without caspase-9]. Autophagy occurs through endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-mediated signaling. Dashed arrows represent putative cross-talk and suggested signaling pathways. EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; SOS, son of sevenless; RalGEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) for the small G protein Ral pathways; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase; ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; TLRs: toll-like receptors; MDA5, melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5; IFN-β, interferon-beta; eIF-2α, eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa light-chain enhancer of activated B cells; IRF-3, interferon regulatory factor 3.