Table 1.
Intron localization of A. thaliana, H. sapiens, and the SPO11 genes from the two fungi C. cinerea (Basidiomycota) and C. grayi (Ascomycota) with respect to their corresponding amino acid sequence positions.
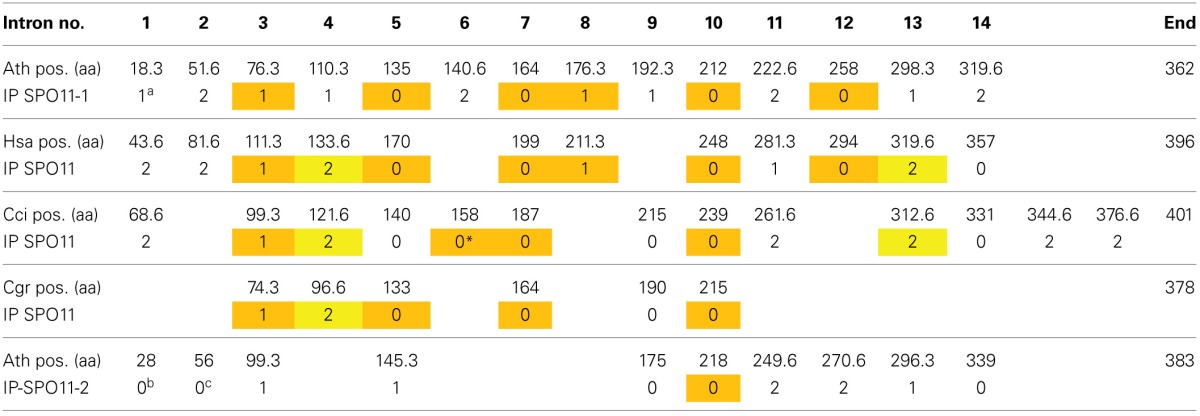
The numbering of introns was done with respect to the highest number of 14 introns in Arabidopsis SPO11-1. Gaps are included in the other lines to better visualize the conserved intron positions.
aThis intron has been lost in Utricularia gibba.
bThis intron has been lost in Fragaria vesca, Malus domestica, Mimulus guttatus, Prunus persica, and Vitis vinifera.
cThis intron has been lost in Oryza brachyantha and Oryza sativa.
*This intron number 5 of C. cinerea is in the same conserved position as intron number 5 of Arabidopsis SPO11-1 and H. sapiens but is preceded by a non-conserved intron position (no. 4).
Color coding: Orange, intron position conserved at least since the split of the plant and animal kingdom, sometimes (8 and 12) lost later on in fungis; Yellow, intron position conserved between H. sapiens (as representative for animals) and two fungal divisions. Abbreviations: IP, Intron position; Ath, Arabidopsis thaliana; Cci, Coprinopsis cinerea; Cgr, Cladonia grayi; Hsa, Homo sapiens.
