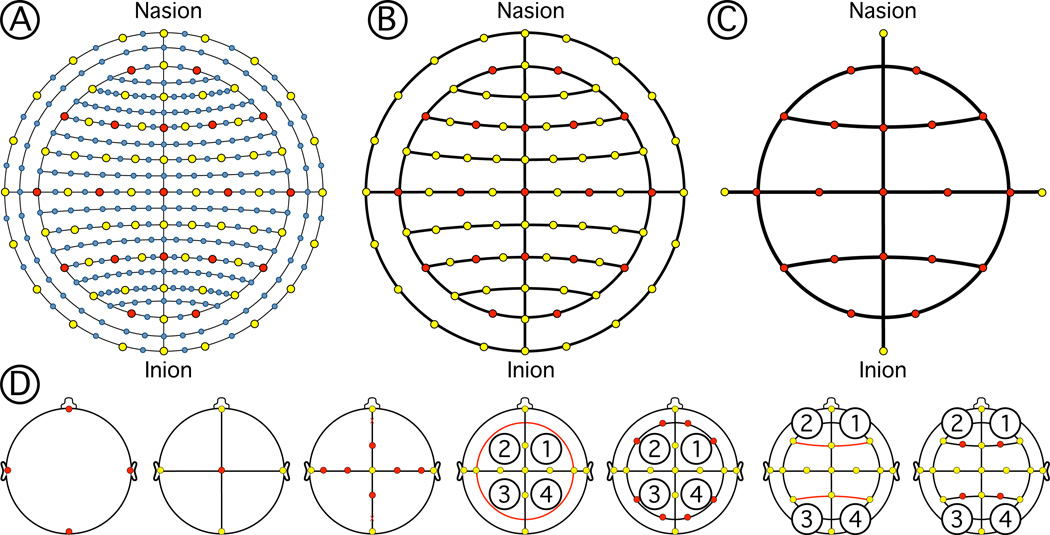
Figure 3.
EEG electrode layouts and positioning algorithm. A) 10-5 positioning system. B) 10-10 positioning system. C) 10–20 positioning system. The set of positions that the software produces are labeled according to the 10-5 nomenclature proposed by Oostenveld and Praamstra (2001). EEG positioning order of operations. D) (From left to right) The fiducials are identified in the head (Nasion, inion, left and right preauriculars). Arcs following the contour of the scalp connect those points. The central position (Cz) is identified at the midpoint of the two arc lengths. EEG locations are identified by percentage subdivisions of the arcs. Locations are used to form new arcs that delimit the circumference of the head. Four quadrant arcs are found connecting those points. Circumference points are calculated from percentage subdivisions of quadrant arcs. Points in the inion-nasion arc and circumference are connected with arcs. EEG positions are found on those arcs by percentage subdivisions.