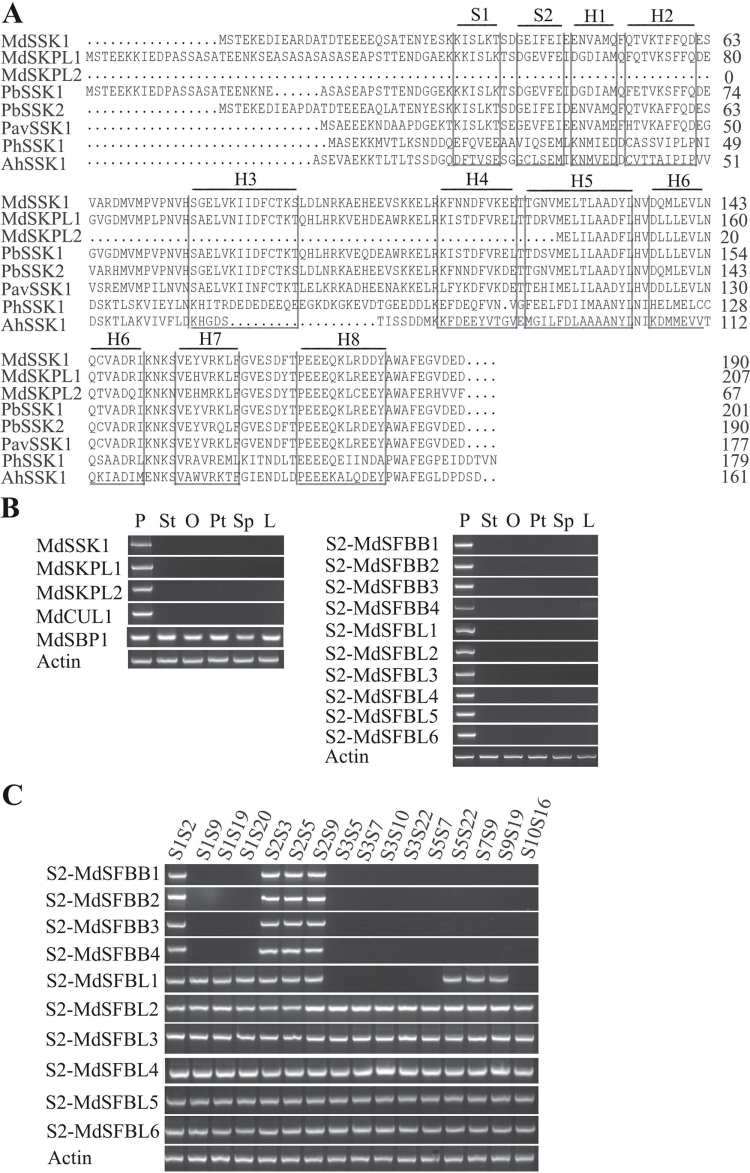
Fig. 1.
Sequence alignment of SSK genes and the expression patterns of the genes in this research. (A) Sequence alignment and structural elements of SSKs. PavSSK1 (JQ322646), PhSSK1 (FJ490176), AhSSK1 (DQ355479), PbSSK1 (HE802072), PbSSK2 (HE802071), MdSSK1, MdSKPL1, and MdSKPL2 are from this study. The boxes represent the secondary structure. S β-sheet, H α-helix. (B) The expression patterns of MdSSK1, MdSKPL1, MdSKPL2, MdCUL1, MdSBP1, S2-MdSFBB1–4, and S2-MdSFBL1–6 were examined by RT-PCR. Total RNAs of different organs were extracted and used as templates for cDNA synthesis and RT-PCR. L (leaves), Sp (sepals), Pt (petals), O (ovaries), St (styles), P (pollen). (C) The haplotype specificity expression patterns of S2-MdSFBB1–4 and S2-MdSFBL1–6 were examined by RT-PCR. Total DNAs of 16 cultivars were extracted and used as templates for RT-PCR.