Figure 3.
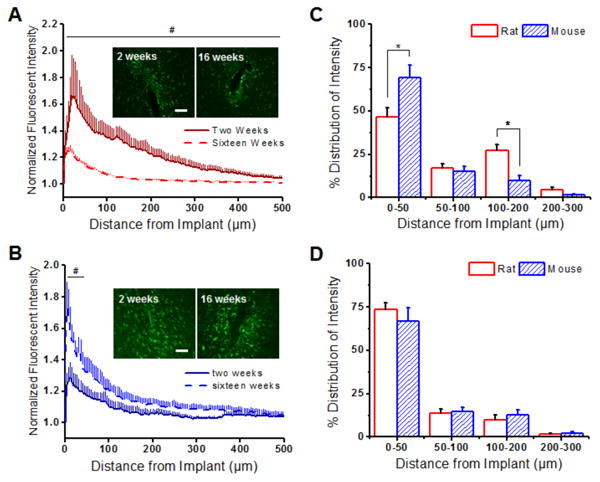
Astrocytic scarring (GFAP+ immunoreactivity) around implanted intracortical microelectrodes in the rat and the mouse model. (A) GFAP+ immunoreactivity was found to be significantly higher up to 500 μm away from the implant at two weeks (solid red) compared to sixteen weeks (dashed red) in the rat model. (B) In contrast, lower GFAP+ immunoreactivity was found within the first 50 μm of the implanted device at two weeks (solid blue) compared to sixteen weeks (dashed blue) in the mouse model. (C) GFAP+ distribution profiles were significantly higher in the mouse model in comparison to the rat model at two weeks from 0-50 μm and 100-200 μm from the microelectrode-tissue interface. (D) By sixteen weeks, similar GFAP+ distribution profiles were observed between the animal models. *p<0.05; Scale = 100 μm; n = 4-7 animals for each cohort
