Fig. 1. The circadian CLOCK network.
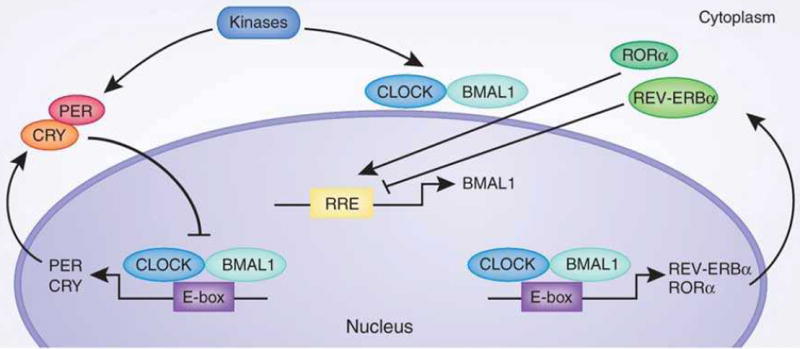
The core circadian transcription factors, CLOCK and BMAL1, direct E-box mediated transcription of clock controlled genes (CCGs), including activators and repressors of the circadian system. PER and CRY protein translation occurs at night and subsequently causes repression of the core CLOCK:BMAL1 transcriptional complex. Degradation of the PER/CRY repressors prompts a new circadian cycle whereby CLOCK:BMAL1 transcription is reinitiated. In addition to transcriptional regulation, post-translational modifications play a critical role in the modulation of circadian proteins. Here only phosphorylation is schematically presented. This can be elicited by a number of kinases including CKIε, CKIδ, CK2α, GSK3β and AMPK. Other post-translational modifications of clock proteins include acetylation, sumoylation and ubiquitination. RRE, REV-ERB/ROR response element; CK, Casein kinase; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta; P, phosphorylation.
