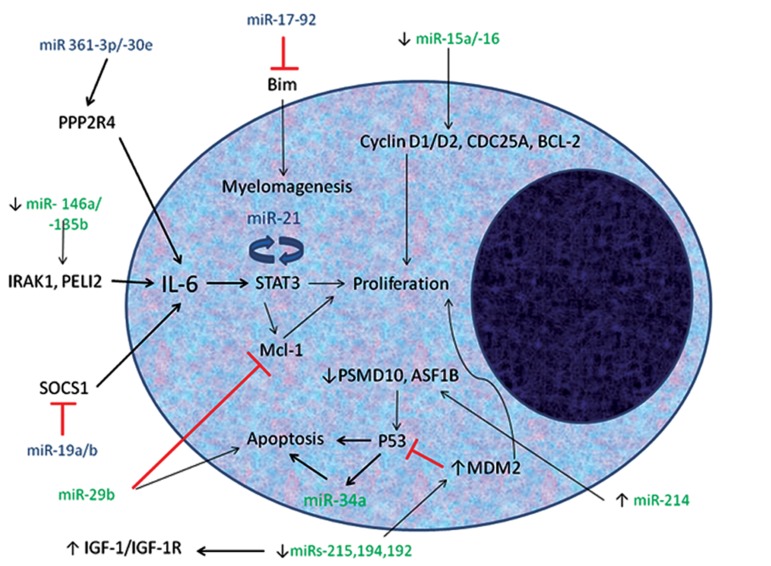
Fig 1.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in pathogenesis of multiple myeloma (MM) by targeting some signaling pathways in myeloma cells. Oncogenic miRNAs are shown in blue and tumor suppressive miRNAs are shown in green. Expression of 361-3p/-30e, 19a/b and 17-92 miRNAs as oncogenes are increased in myeloma cells. The first two miRNAs respectively target the PPP2R4 and SOCS1 genes and activate the IL-6 signaling pathway, eventually augmenting the growth of myeloma cells. Expression of 17-92 miRNA in myeloma cells prevents their apoptosis by reduced expression of Bim. -15a/-16, -215-194-192, -146a/-135b,-34a,-29b and -214 miRNAs have been identified as tumor suppressors in MM. Decreased level of -215-194-192, -146a and -15a/-16 miRNA results in increased expression of MDM2, IRAK1/PELI2 and cyclin D1/D2, respectively, with increased growth of myeloma cells as a result. Increased miRNA-214 can induce the expression of p53 and apoptosis of myeloma cells by reducing the expression of PSMD10 and ASF1B. Expression of miRNA-29b and miRNA-34a are decreased in myeloma cells; miRNA-29b causes apoptosis by reducing expression of Mcl-1 involved in the IL-6 pathway.
IRAK1;IL-1 receptor associated kinase, PELI2; Protein pellino homolog 2, SOCS1; Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1, IGF- 1/IGF-1R; Insulin-like growth factor/receptor, MCL-1; Myeloid-cell-leukemia, MDM2; Mouse double minute 2 homolog, CDC25A; Cell division cycle 25 homolog A, BCL-2; B-cell lymphoma 2, PPP2R4; Protein phosphatase 2 activator regulatory subunit 4 and ASF1B; Anti-silencing function 1 homolog B.