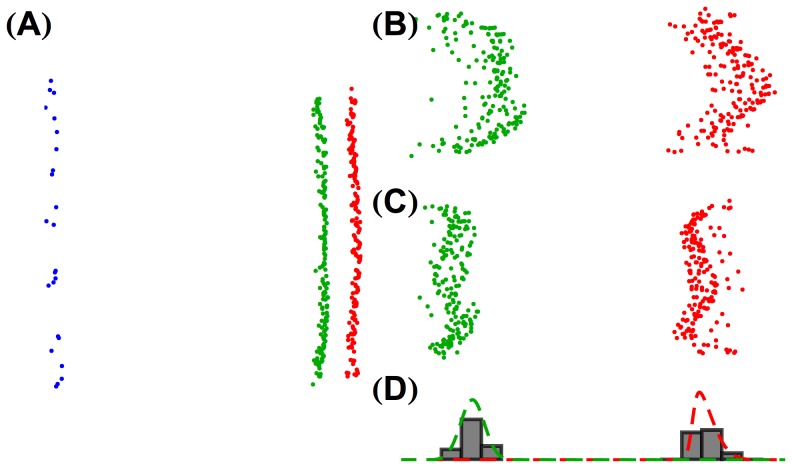
Figure 3. Multidimensional scaling allows classification of cones for a typical trichromatic retinal mosaic.
(A) 3D embeddings of the correlation matrix of the 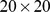 mosaic from Figure 2A. Each point represents a single cone and is colored red, green, or blue for L, M, or S respectively, according to its actual identity in the mosaic. The 3D embeddings shown here and in other figures in this paper are oriented so that the
mosaic from Figure 2A. Each point represents a single cone and is colored red, green, or blue for L, M, or S respectively, according to its actual identity in the mosaic. The 3D embeddings shown here and in other figures in this paper are oriented so that the  -
-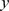 plane (
plane ( horizontal,
horizontal, 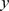 vertical) of the representational space described in the text is shown. The absolute units on these axes are not meaningful, because MDS solutions are determined only up to a relative-distance preserving transformation. (B) The same 3D embedding shown in A zoomed in on the embedding of the L and M cones only. (C) The 3D embedding of the L and M cones from A after flattening. (D) A histogram of the
vertical) of the representational space described in the text is shown. The absolute units on these axes are not meaningful, because MDS solutions are determined only up to a relative-distance preserving transformation. (B) The same 3D embedding shown in A zoomed in on the embedding of the L and M cones only. (C) The 3D embedding of the L and M cones from A after flattening. (D) A histogram of the  positions of the embedding from C (i.e., after flattening); best fit skew normals are shown in red and green. Rotating animations that show the three-dimensional structure of the embeddings are available online (http://color.psych.upenn.edu/supplements/receptorlearning).
positions of the embedding from C (i.e., after flattening); best fit skew normals are shown in red and green. Rotating animations that show the three-dimensional structure of the embeddings are available online (http://color.psych.upenn.edu/supplements/receptorlearning).