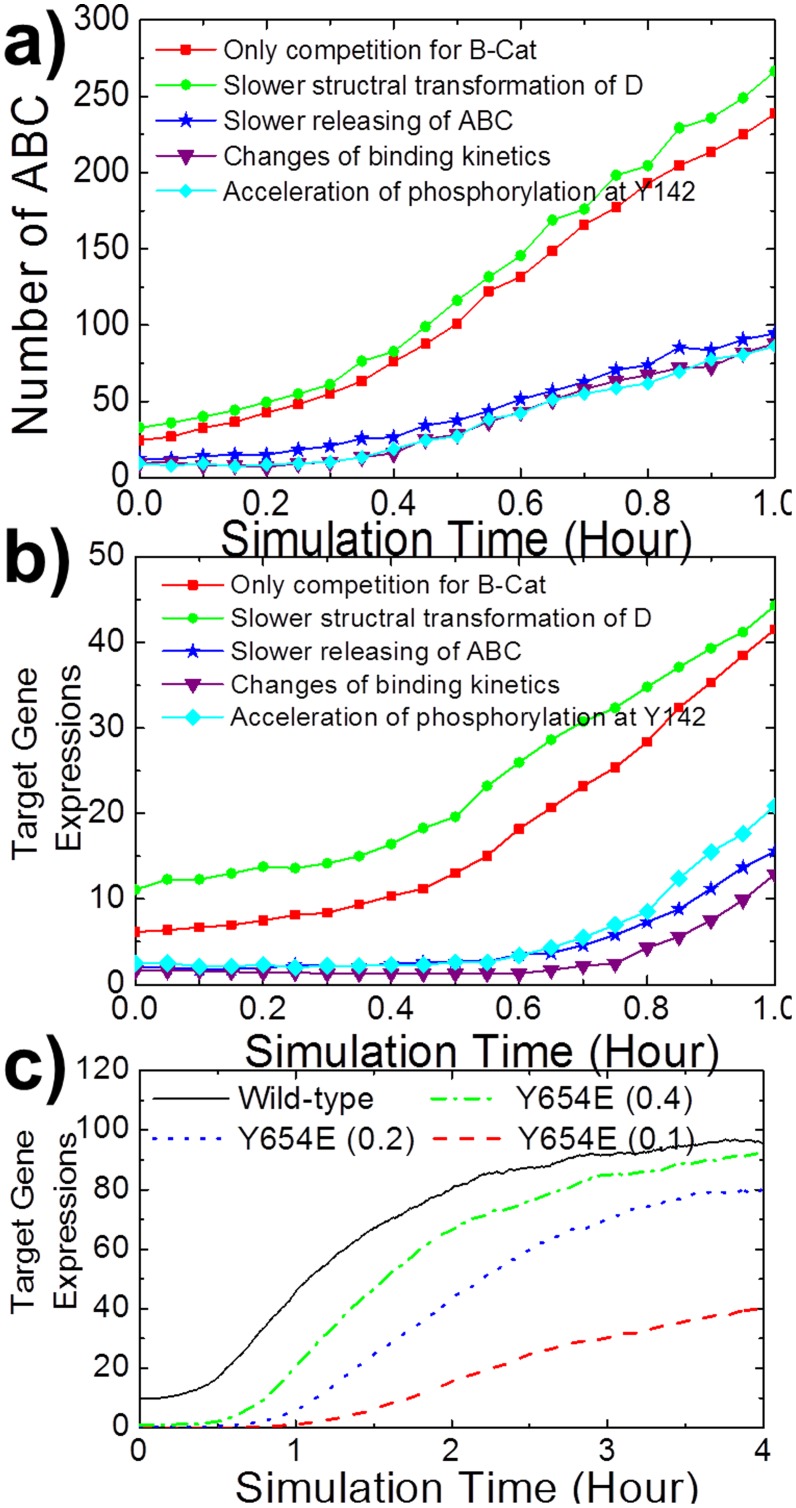
Figure 8. Cell adhesion changes β-catenin distributions under Wnt stimulations.
The values α2 = 0.4 and α1 = 1.5 were chosen. In order to minimize the complexity, we decomposed the multiple factors caused by adhesion and added them step by step. The number of ABC and activated target genes are shown in a) and b). We suggest that slow releasing of ABCs from destruction complexes is the major factor cause by cell adhesion. We further proposed that cell adhesion also affects Wnt signaling by regulating the phosphorylation rate of β-catenins. Given the truth that the mutant of Y654 reduces the binding affinity between cadherin and β-catenin and decrease the phosphorylation rate of Y142, we set the Y142 phosphorylation rate of Y654 mutant equals to 0.4, 0.2 and 0.1 of the original value in wild-type β-catenin c). We found that the Wnt target gene expressions of Y654 mutants are reduced. All curves were averaged over 50 simulation trajectories.