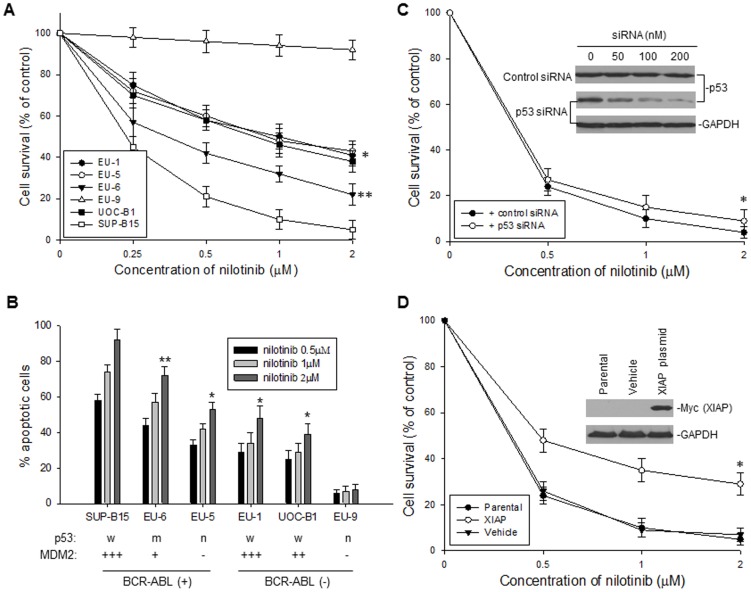
Figure 4. Cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of nilotinib on ALL cells.
A, dose-dependent cytotoxic response to nilotinib in the six ALL cell lines, as tested for Fig. 1A. The viability of cells incubated with different concentrations of nilotinib for 24 h was determined by WST assay. Data from three independent experiments is represented by the mean percentage ± SD of surviving cells, as compared to the untreated controls. *p<0.01; **p<0.05 (as compared with SUP-B15) B, dose-response of apoptosis of the six cell lines treated with the nilotinib doses indicated for 24 h, as quatitatively detected by flow cytometry. *p<0.01; **p<0.05 (as compared with SUP-B15). C, the effect of p53 knockdown on sensitivity of BCR-ABL+ cells to nilotinib. SUP-B15 cells, transfected with 200 nM of either p53 siRNA or control siRNA, were treated with different dose of nilotinib for 24 h, and cell viability was detected by WST assay, *p>0.5. The expression of p53 in SUP-B15 cells transfected with p53 siRNA was determined by Western blot assay (insert). D, the effect of enforced overexpression of XIAP on sensitivity of ALL cells to nilotinib. SUP-B15 cells, transfected with pCDNA3-6myc-XIAP plasmid and vehicle control, were treated with different dose of nilotinib for 24 h, and cell viability was detected by WST assay, *p<0.05. Western blot showing the expression of ectopic XIAP (as detected by Myc antibody) in SUP-B15 cells (insert).