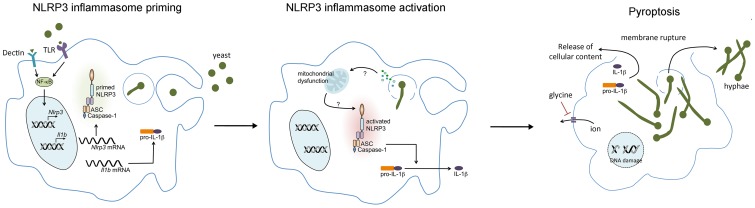
Figure 1. C. albicans–mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
Upon encountering C. albicans, pattern recognition receptors (PRR) on the macrophage, such as TLR2 and Dectin 1 and 2, activate NF-κB, leading to the transcription and translation of NLRP3 and pro-IL-1β. Phagocytosis of C. albicans yeast forms triggers hyphal formation which may result in lysosomal rupture. NLRP3 inflammasome activation is then triggered through an as-yet-undefined mechanism. Although morphogenesis appears to be necessary for inflammasome activation, it is not sufficient. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome results in activation of the cysteine protease caspase-1, which mediates the processing and secretion of pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18. Caspase-1 activation also induces pyroptotic cell death of the macrophage, resulting in cell swelling, DNA fragmentation, and the lytic release of intracellular inflammatory contents. Osmotic lysis of the macrophage during pyroptosis can be inhibited by the addition of extracellular glycine.