Figure 3.
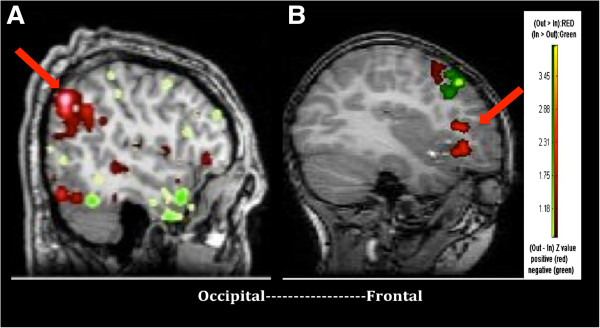
Subset of regions of network of greatest average coherence in a representative ASD and NT participant. Red reflects sending of information while green reflects receiving of information flow in areas of high average coherence. In a male adolescent with ASD (A), information in posterior cortical areas (parietal cortex) is highly active in sending information when processing eye gaze cues while minimal frontal activity is noted. In a NT adolescent male (B), the left inferior and middle frontal gyri are highly active in sending information when processing gaze cues.
