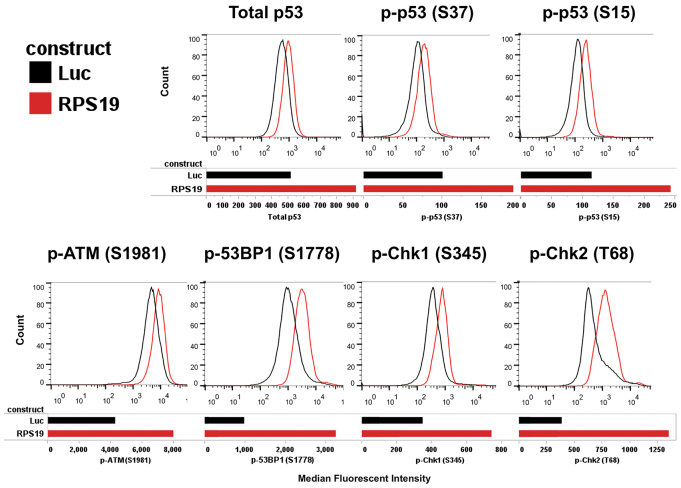
Fig. 4.
Human RPS19 deficient cells have an activated DNA damage checkpoint. Intracellular phosphoflow cytometry of RPS19-deficient human CD34+ cells from fetal liver 5 days after transduction with lentiviral vectors expressing shRNA against RPS19. A vector targeting luciferase was used as a control. All vectors also expressed GFP. Histograms show GFP-positive gated cells from luciferase control (Luc, black) or RPS19-knockdown cells (RPS19, red). Bar graphs show the median fluorescent intensity obtained from the histograms for each antibody-fluorochrome conjugate. We used primary antibodies against phosphorylated p53 at residue S37 [p-p53 (S37)], total p53, phosphorylated p53 at residue S15 [p-p53 (S15)] that were conjugated to Alexa Fluor 647. We also used the following unconjugated antibodies: mouse against phosphorylated ATM at residue S1981 [p-ATM (S1981)], rabbit against phosphorylated 53BP1 at residue S1778 [p-53BP1 (S1778)], rabbit against phosphorylated Chk1 at S345 [p-Chk1 (S345)], and rabbit against phosphorylated Chk2 at T68 [pChk2 (T68)] with a secondary labeling step using either anti-mouse IgG antibody conjugated to PE or anti-rabbit IgG antibody conjugated to PE.