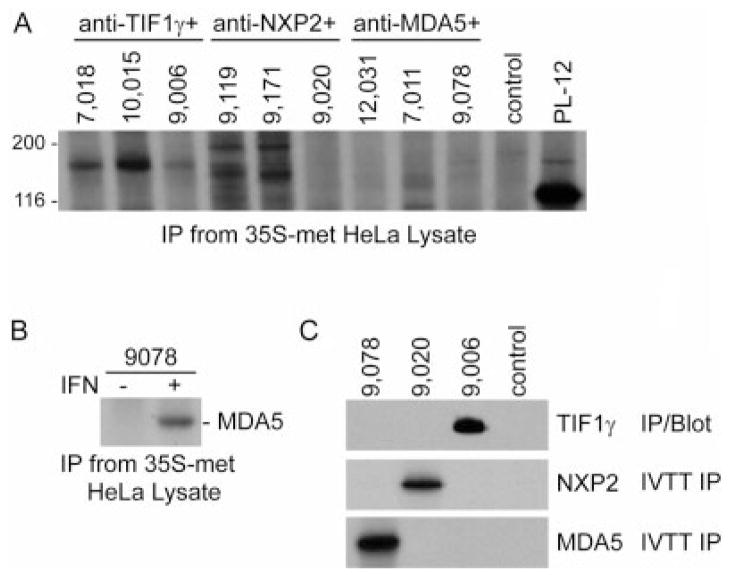
Figure 1.
New assays to detect antibodies against transcription intermediary factor 1γ (TIF-1γ), nuclear matrix protein NXP-2, and melanoma differentiation–associated protein 5 (MDA-5). A, Immunoprecipitations (IP) were performed using 35S-methionine (35S-met)–labeled HeLa cell lysate with patient sera known to have antibodies against TIF-1γ, NXP-2, or MDA-5, as indicated (3 sera for each). A control serum and an alanyl–transfer RNA synthetase (PL-12)–positive reference serum were also included. B, Immunoprecipitations were performed with an anti–MDA-5 antibody–positive serum using 35S-methionine–labeled HeLa cell lysate generated from cells incubated in the absence or presence of interferon (IFN) for 24 hours. C, Three sera from patients with dermatomyositis and 1 control serum were tested for antibodies by immunoprecipitation using 35S-methionine–labeled MDA-5 or 35S-methionine–labeled NXP-2 (in vitro transcription/translation immunoprecipitation [IVTT IP]), or by immunoprecipitation from TIF-1γ–transfected lysates followed by immunoblotting with anti–TIF-1γ monoclonal antibody (IP/Blot). These assays show that serum 9,078 is anti–MDA-5 positive, serum 9,020 is anti–NXP-2 positive, and serum 9,006 is anti–TIF-1γ positive.