Fig. 7.
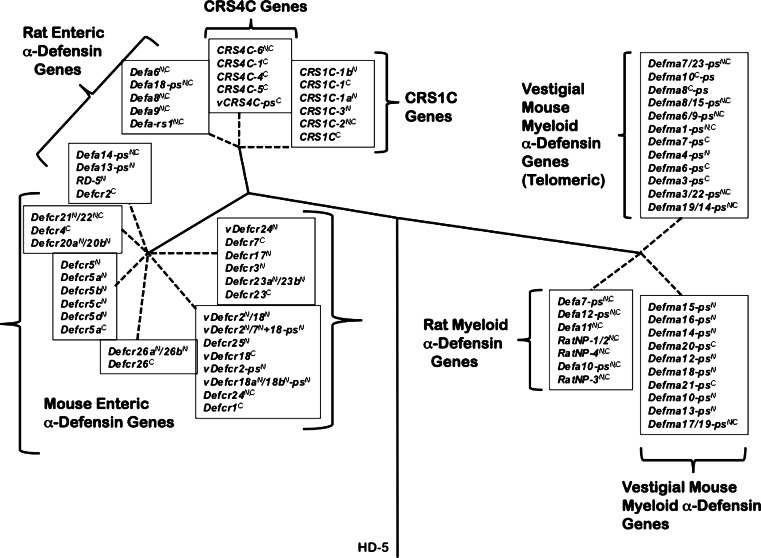
Phylogenetic relationships between rat and mouse α-defensin, CRS1C, and CRS4C genes. The introns of mouse Paneth cell α-defensin, CRS1C and CRS4C genes from the NIH C57BL/6 and the mixed strain Celera assemblies, introns of rat enteric α-defensin genes, and second introns of rat myeloid α-defensin genes, and vestigial mouse myeloid α-defensin (DefmaN-ps) genes were used to construct the phylogenetic tree. The tree was rooted with the intron of the human α-defensin-5 (HD-5) gene, and construction of the tree involved the calculation of the proportion difference (p-distance) of aligned nucleotide sites of the entire intron sequences according to the neighbor-joining method. One thousand bootstrap replications were used to test the reliability of each branch. Solid lines maintain phylogenetic distances, but dashed lines do not in order to maintain legibility of sequences of the tree. Reprinted from [90], with permission