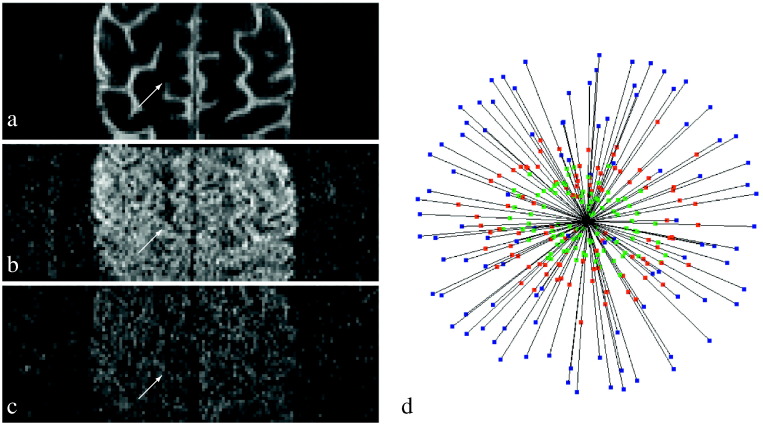
Fig. 1.
Diffusion weighted data S for an arbitrarily selected slice of the multi-shell data described in Methods. a) Slice of the non-diffusion weighted data. b) Same slice taken with diffusion-weighting gradient and b-value b = 800s/mm2. c) Same slice taken with the same gradient and b-value b = 2000s/mm2. The intensity of the diffusion weighted images in (b + c) has been up-weighted to make all three images visually feasible at once. d) Shows the data within a single voxel (see arrow) as a 3D plot for all measured diffusion gradients in red and green at b = 800s/mm2 and b = 2000s/mm2, respectively. For comparison the non-diffusion weighted value is repeatedly shown as blue point for each gradient. The distance of the points to the center of the sphere is the corresponding signal value. Each 3D diffusion weighted image (a–c) is fully described by the set of signals in voxel space for a fixed diffusion gradient direction (if b ≠ 0) and the b-value b ∈ B0. Conversely, the data in a single voxel equals the set of vectors, see (d).