Figure 1. PRMT4 regulates myeloid differentiation of HSPCs.
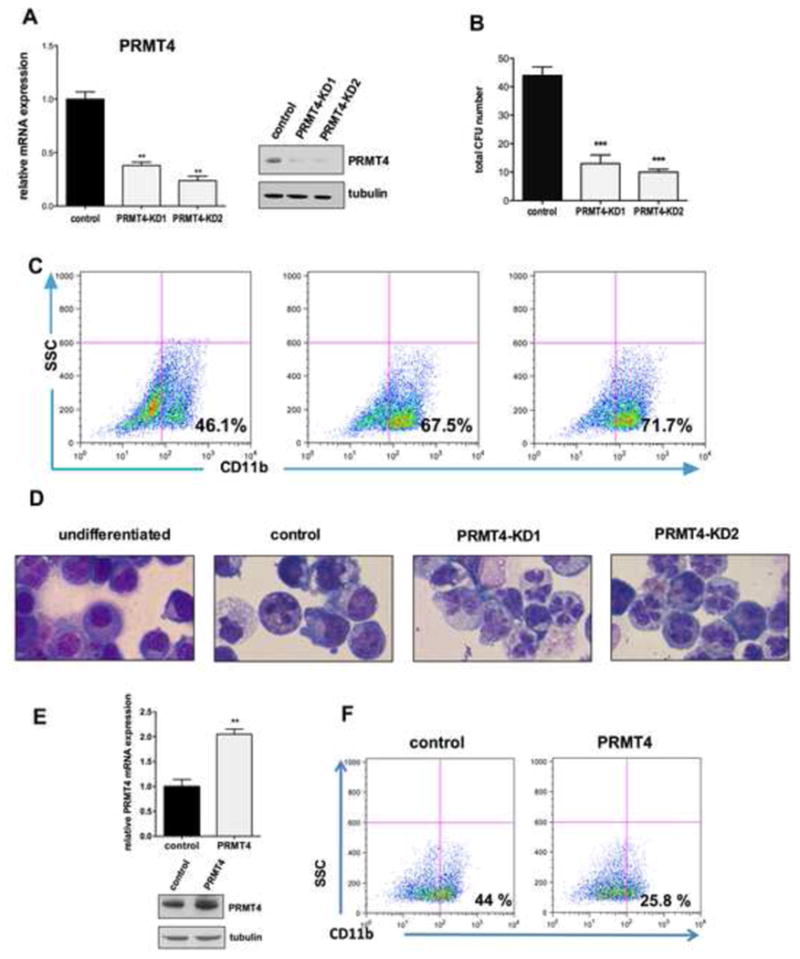
(A). Efficient knock down of PRMT4. Human CB CD34+ cells were transduced with lentiviruses expressing a control (scrambled) shRNA or one of two shRNAs directed against PRMT4. GFP-positive cells were sorted 3 days after transfection and collected to perform qRT-PCR and Western blot analyses. qRT-PCR data represents the mean ± SD of the three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 by Student's t test. Tubulin served as the loading control.
(B). Downregulation of PRMT4 decreases CFU formation. 104 of the control or PRMT4 knock down cells were plated in methylcellulose. The total number of colony forming units (CFUs) was scored 2 weeks after the plating. The data represents the mean ± SD of the three independent experiments. *** p < 0.001 by Student's t test.
(C). Downregulation of PRMT4 promotes the myeloid differentiation of HSPCs. GFP+ CD34+ cells were cultured in myeloid-promoting cytokine containing medium for 7 days. Myeloid differentiation was determined by FACS analysis of CD11b expression.
(D). Downregulation of PRMT4 promotes the myeloid differentiation of HSPCs. Cellular morphology was evaluated after 7 days in myeloid-promoting cytokine containing medium. Cells growing in basic culture were used as the control for myeloid differentiation.
(E). Overexpression of PRMT4 was demonstrated at the mRNA and protein levels. Human CB CD34+ cells were transduced with retroviruses expressing either control (GFP alone) or GFP and HA-PRMT4. GFP+ cells were sorted after 3 days of transfection and collected to perform qRT-PCR and Western blot analyses. qRT-PCR data represents the mean ± SD of the three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 by Student's t test.
(E). Overexpression of PRMT4 blocks the myeloid differentiation of HSPCs. GFP+ CD34+ cells were cultured in myeloid-promoting cytokine containing medium for 7 days. Myeloid differentiation was determined by FACS analysis of CD11b expression.
See also Figure S1.
