Figure 4. RUNX1 is arginine methylated by PRMT4 on R223.
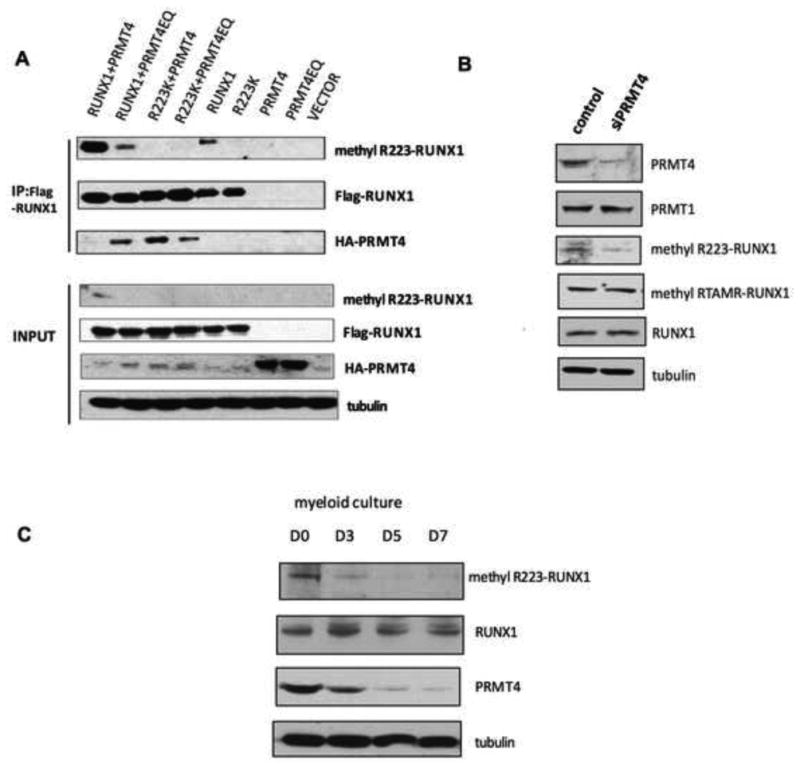
(A). In vivo methylation of RUNX1 by PRMT4 was detected using a methyl-RUNX1 specific antibody. The full-length Flag- RUNX1 or Flag- RUNX1-R223K mutant cDNAs were overexpressed in 293T cells, with or without HA-tagged-WT-PRMT4, or an enzymaticallly dead PRMT4 mutant (PRMT4EQ). Immunoprecipitation was performed using an anti-Flag antibody and immunoblotting with anti-FLAG or anti-HA antibodies. Wild type RUNX1 (lane 1 and 2), but not the R223K mutant protein (lane 3 and 4) is methylated by wild type PRMT4. The physical interaction between RUNX1 and PRMT4 is detected when RUNX1 is overexpressed with PRMT4EQ, but not WT-PRMT4, and when R223K is overexpressed with PRMT4 or PRMT4EQ (lanes 1-4 in the third row). Tubulin served as the loading control.
(B). Knock down of PRMT4 in HEL cells using siRNA reduces the level of endogenous methylR223-RUNX1, without altering total RUNX1 levels or the methylation of RUNX1 at the RTAMR motif.
(C). The level of RUNX1R223 methylation decreases during myeloid differentiation, without changes in total RUNX1 expression but concordant with changes in PRMT4 protein levels.
See also Figure S4.
