Figure 6. The RUNX1 methylation dependent repressor complex regulates miR-223 expression.
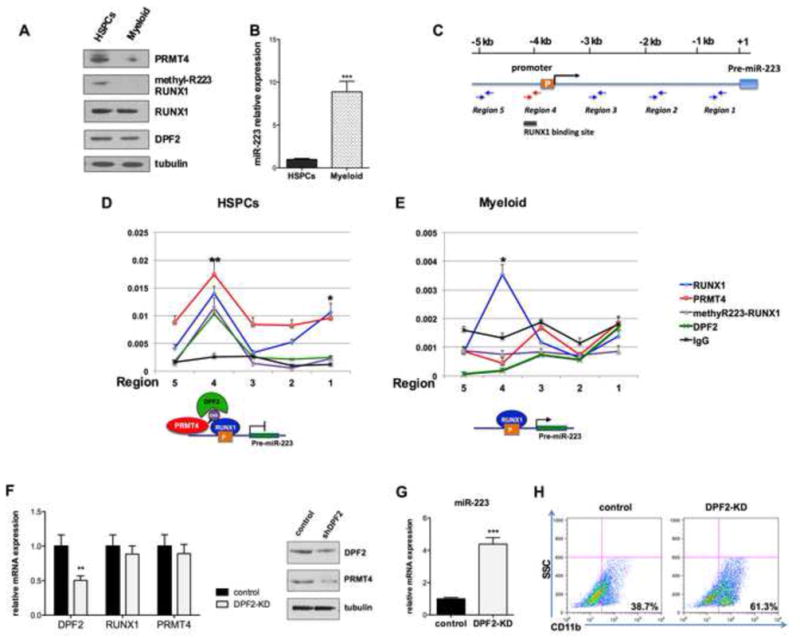
(A). Western blot analysis quantified the levels of expression of PRMT4, methyl R223-RUNX1, RUNX1 and DPF2 in CD34+ cells maintained in basic culture or in cells cultured in myeloid differentiation-promoting medium for 7 days. Tubulin served as the loading control.
(B). The level of miR-223 expression in the HSPCs and myeloid differentiated cells. qRT-PCR data represents mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *** p < 0.001 by Student's t test.
(C). A schematic diagram of the miR-223 promoter. The location of the RUNX1 consensus binding sites and the primers used for the ChIP assays is shown.
(D). (E). ChIP assays show the presence of a methyl-R223 RUNX1- dependent complex at the promoter of miR-223 in HSPCs (D), but not in myeloid differentiated cells (E). Upper panel: Enrichment of proteins of interest at miR-223 regulatory regions was assayed by qRT-PCR and shown as percentage of the genomic input DNA. * p < 0.5; ** p < 0.01 by Student's t test.
Lower panel: diagrams demonstrating the recruitment of RUNX1, methylR223-RUNX1 and DPF2 to the miR-223 promoter.
(F). Efficient knock down of DPF2. CD34+ cells were transduced with lentiviruses expressing a control (scrambled) shRNA or shRNA directed against DPF2. GFP-positive cells were sorted 3 days after transfection and collected to perform qRT-PCR and Western blot analyses. qRT-PCR data represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 by Student's t test.
(G). Downregulation of DPF2 increases miR-223 expression. qRT-PCR analysis of miR-223 in control and DPF2 knock down CD34+ cells. The data represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *** p < 0.001 by Student's t test.
(H). Downregulation of DPF2 accelerates the myeloid differentiation of HSPCs. GFP+ CD34+ cells were cultured in myeloid differentiation promoting medium for 7 days. Myeloid differentiation was determined by FACS analysis of CD11b expression.
See also Figure S6.
