Figure 7. Downregulation of PRMT4 is sufficient to induce myeloid differentiation in leukemia cells.
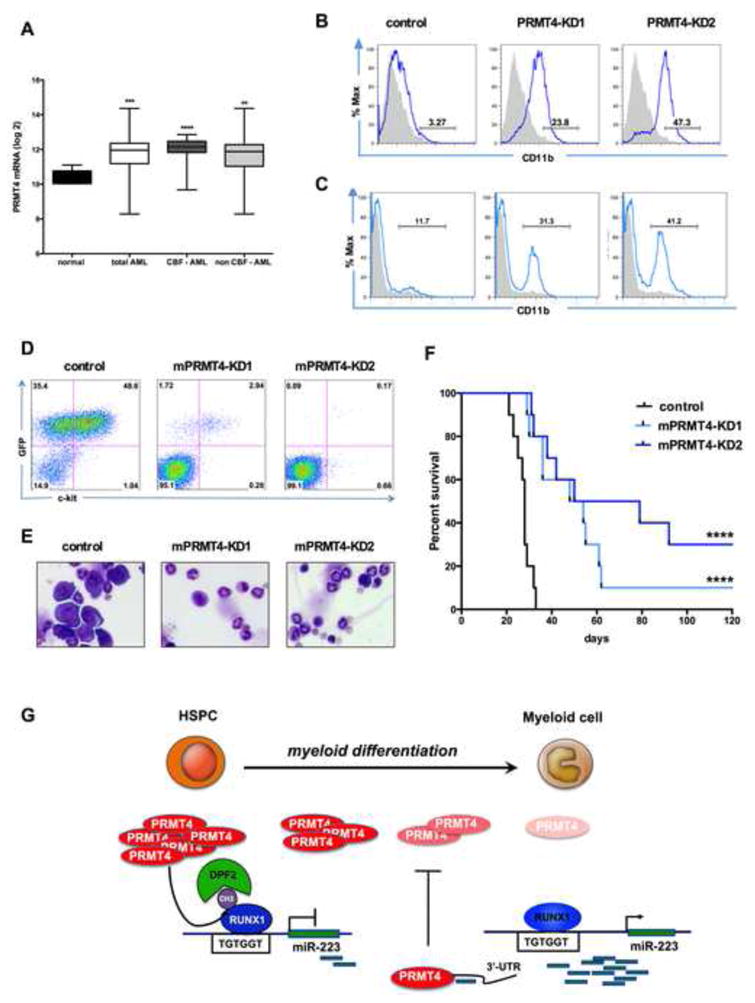
(A). PRMT4 expression is upregulated in AML patient samples. The graph shows the log2 expression of PRMT4 from transcript profiling of CD34+ bone marrow cells isolated from 5 healthy donors (normal) or 318 AML patients. CBF: core-binding factor. CBF-AML n=57. non CBF-AML n=261. **** p < 0.0001 *** p < 0.001 ** p < 0.01 by Student's t test.
(B). Knock down of PRMT4 triggers the myeloid differentiation of NB4 cells. NB4 cells were transduced with lentiviruses expressing control (scrambled) shRNA or shRNA directed against PRMT4. Sorted GFP positive cells were cultured for 3 days prior to FACS analysis of CD11b expression. Quantitative data in Figure S7D.
(C). Knock down of PRMT4 triggers the myeloid differentiation of Kasumi-1 cells. Kasumi-1 cells were transduced with lentiviruses expressing control (scrambled) shRNA or shRNA directed against PRMT4. Sorted GFP positive cells were cultured for 3 days prior to FACS analysis of CD11b expression. Quantitative data in Figure S7D.
(D). FACS analysis showed far fewer GFP+ ckit + cells in peripheral blood (PB) of the mice transplanted with AE9a – mPRMT4-KD cells in compare to AE9a – control cells at week 3. AE9a expressing mouse leukemia cells were transduced with shRNA scramble control (AE9a-control), or shRNAs against PRMT4 (AE9a-mPRMT4-KD1 and mPRMT4-KD2). Transduced cells were sorted for expression of RFP and the sorted cells were injected into recipient mice that had received sublethal irradiation.
(E). Bone marrow (BM) morphology shows marked reduction in the number of leukemic cells in mice transplanted with AE9a -mPRMT4-KD cells, compared to AE9a- control cells.
(F). Knock down of PRMT4 prolongs the survival of AE9a transplanted mice. The median survival was extended in the knock down groups, compared to the control group (54 days and 64.5 days vs. 28 days p <0.0001).
(G). A schematic model showing how PRMT4 regulates myeloid differentiation of human HSPCs. PRMT4 and miR-223 form a regulatory loop that is critical for myeloid differentiation. PRMT4 inhibits myeloid differentiation by assembling a methyl R223-RUNX1-DPF2 repressor complex that suppresses miR-223 expression. When HSPCs undergo myeloid differentiation, PRMT4 expression is downregulated, releasing the miR-223 locus from transcription repression, allowing it to be transcribed. At that stage, the higher expression of miR-223 targets the PRMT4 3′-UTR to further decrease PRMT4 expression, thereby reinforcing the myeloid differentiation process.
See also Figure S7.
