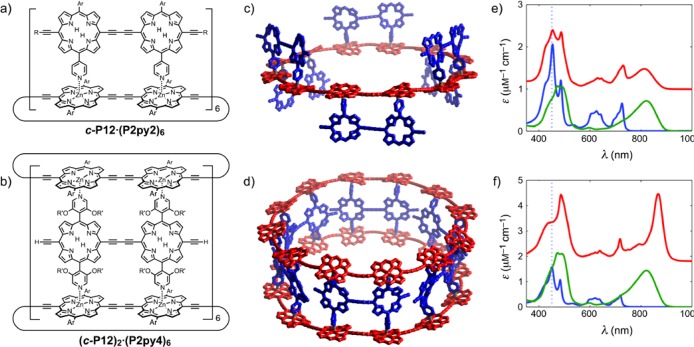
Figure 1.
(a, b) Chemical structures and (c, d) structural models of the ring–dimer complex c-P12·(P2py2)6 (top) and the ring–dimer–ring complex (c-P12)2·(P2py4)6 (bottom). Ar = 3,5-bis(trihexylsilyl)phenyl, R = trihexylsilyl, R′ = dodecyl. (e, f) Plots of the molar absorption coefficients of the components in toluene/1% pyridine (dimer in blue, c-P12 nanoring in green), scaled for their relative numbers within the complex, as functions of wavelength. The absorption spectra of the two complexes in toluene (solid red lines, offset for clarity) are also shown. The excitation wavelength used for PL measurements (450 nm) is indicated as a dashed vertical blue line. The models shown in (c) and (d) are energy-minimized geometries calculated using the mm+ force field in HyperChem.