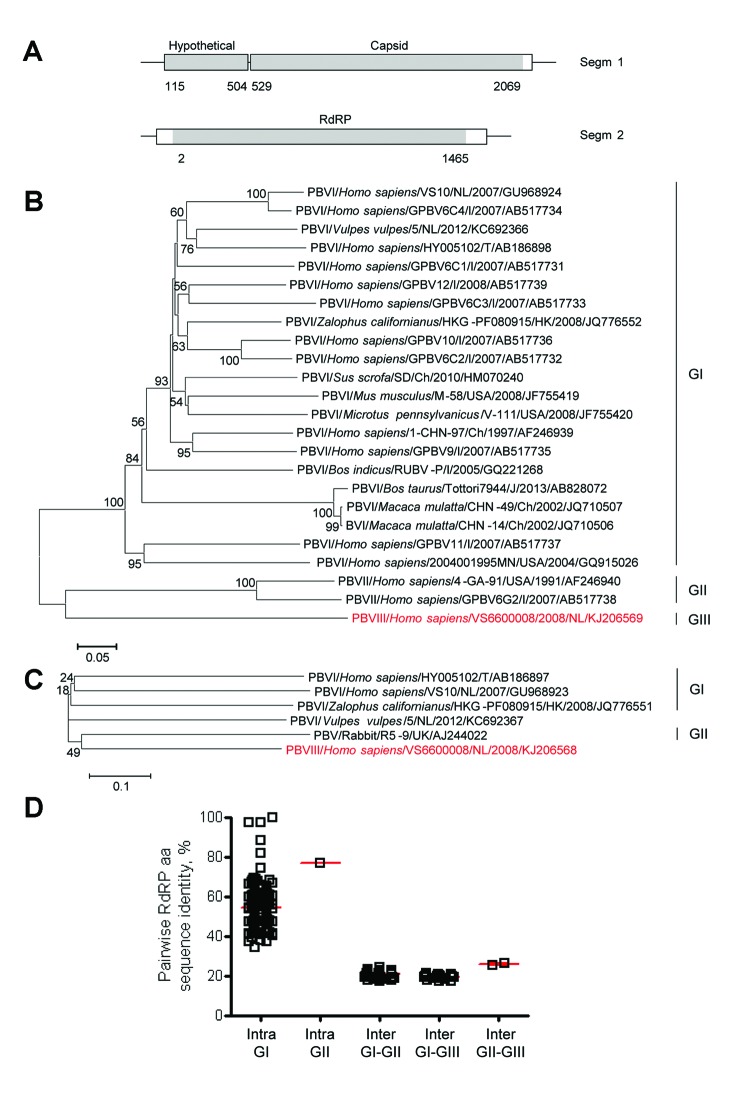
Figure 1.
Genome organization and phylogenetic analysis of human picobirnavirus (PBV) VS6600008 isolated in the Netherlands, 2005–2009. A) Putative schematic genome organization of human PBV VS6600008. Locations of major open reading frames are indicated in white and sequences obtained by next-generation sequencing are indicated in gray. Segm, segment; RdRP, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. B) Phylogenetic neighbor-joining tree with p-distances and 1,000 bootstrap replicates of amino acid sequences of partial RdRP genes corresponding to aa 80–377 of reference PBV strain HY005102; AB186898, PBV VS6600008, and representative PBVs. Alignments were created by using ClustalX 2.0 (http://www.clustal.org/). Viruses are shown as virus/host species/strain/country/year/GenBank accession no. (if available). Virus isolated in this study is indicated in red. Genogroups are indicated on the right. Scale bar indicates amino acid substitutions per site. NL, the Netherlands; I, India; T, Thailand; Ch, China; USA, United States; UK, United Kingdom; J, Japan; HK, Hong Kong. C) Phylogenetic neighbor-joining tree with p-distances and 1,000 bootstrap replicates of the amino acid sequences of the partial capsid genes corresponding to aa 1–220 of reference PBV strain HY005102; AB186897, PBV VS6600008, and representative PBVs. Alignments were created by using ClustalX 2.0. Virus isolated in this study is indicated in red. Genogroups are indicated on the right. Scale bar indicates amino acid substitutions per site. D) Pairwise intragenogroup (Intra) and intergenogroup (Inter) amino acid sequence identities determined by using Bioedit 7.0.9.0 (http://www.mbio.ncsu.edu/bioedit/bioedit.html) between the partial RdRP sequences (corresponding to amino acids 80–377 of reference PBV strain HY005102; AB186898). Each square represents pairwise RdRP amino acid sequence identity between viruses in panel B. Red bars indicate mean and SEM.