FIGURE 2.
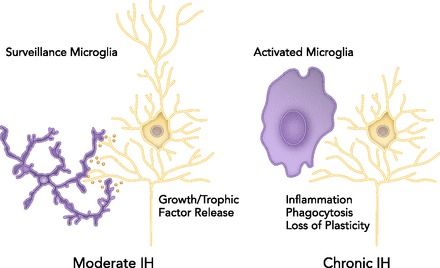
In the healthy CNS with no, or “low-dose” IH, microglia are in a “surveillance mode” that promotes neuron viability and function by releasing growth/trophic factors that confer neuro-protection and/or increase synaptic strength (i.e., plasticity)
In contrast, high doses of IH, such as chronic IH, may activate microglia to a toxic, pro-inflammatory phenotype that triggers neuronal apoptosis and undermines synaptic plasticity.
