Fig. 3.
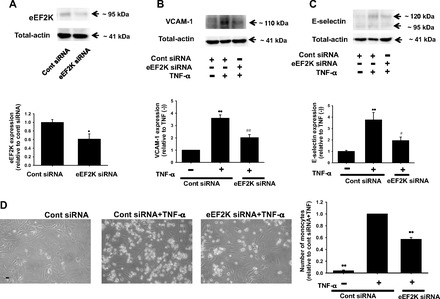
Effects of eEF2K gene knockdown on TNF-α-induced inflammatory responses in HUVECs. Knockdown of eEF2K gene by small interfering RNA (siRNA) is shown (A). After HUVECs were transfected with eEF2K-specific siRNA (eEF2K siRNA) or nonsilencing control siRNA (40 nmol/l; 24 h), total cell lysates were harvested. Expression of eEF2K protein (n = 6) was determined by Western blotting and shown as fold change relative to control siRNA. Equal protein loading was confirmed using total-actin antibody. *P < 0.05 vs. control siRNA. Effects of eEF2K knockdown on TNF-α-induced expression of VCAM-1 (B) and E-selectin (C) are also shown. After HUVECs were transfected with eEF2K siRNA or control siRNA, they were treated with 10 ng/ml TNF-α for 6 h. Expression of VCAM-1 (n = 4) and E-selectin (n = 6) was determined by Western blotting and shown as fold increase relative to control siRNA without TNF-α stimulation. Equal protein loading was confirmed using total-actin antibody. **P < 0.01 vs. control siRNA without TNF-α stimulation; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. cont siRNA + TNF-α. Effects of eEF2K knockdown on monocyte (U937 cells) adhesion to HUVECs (D) are also shown. After HUVECs were transfected with eEF2K siRNA or control siRNA, TNF-α (10 ng/ml, 6 h) was treated. After U937 cells were added for 1 h to HUVECs (n = 4), nonadherent cells were removed and the number of adhering U937 cells was randomly counted in 3 areas (×200 fields) and averaged. Scale bar, 50 μm. The number of U937 cells adhering to HUVECs was shown as fold increase relative to control siRNA with TNF-α stimulation. **P < 0.01 vs. cont siRNA + TNF-α.
