Fig. 4.
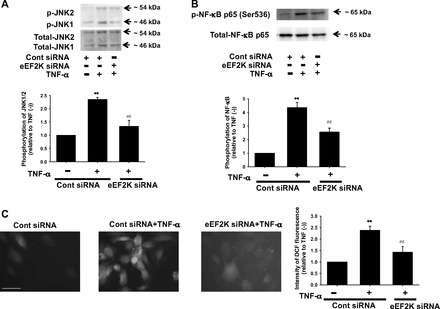
Effects of eEF2K knockdown on TNF-α-induced phosphorylation of JNK (A) and NF-κB (B), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (C) in HUVECs. After transfection with eEF2K siRNA or control siRNA (40 nmol/l, 24 h), HUVECs were stimulated with 10 ng/ml TNF-α for 20 min. Phosphorylation of JNK (n = 4) and NF-κB p65 (Ser536) (n = 4) was determined by Western blotting and shown as fold increase relative to control siRNA without TNF-α stimulation. Equal protein loading was confirmed by using total antibody. ROS production was determined by a fluorescence staining using 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (H2DCFDA). After HUVECs were treated with 10 ng/ml TNF-α for 20 min in the presence of eEF2K siRNA or control siRNA (n = 4), they were loaded with H2DCFDA (10 μmol/l) for 30 min. Images were obtained using a fluorescence microscope. Scale bar, 50 μm. Fluorescent intensity was measured using ImageJ software and shown as fold increase relative to control siRNA without TNF-α stimulation. **P < 0.01 vs. control siRNA without TNF-α; ##P < 0.01 vs. cont siRNA + TNF-α.
