Fig. 7.
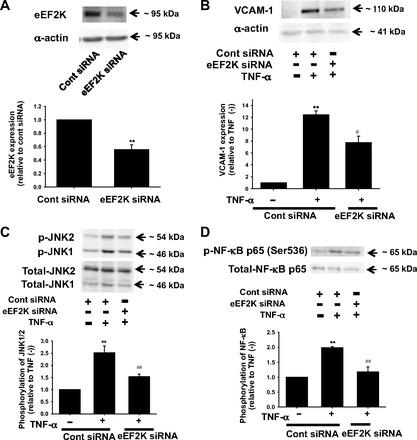
Effects of eEF2K knockdown on TNF-α-induced inflammatory responses in rat mesenteric arterial smooth muscle cells (SMCs). Knockdown of eEF2K gene by siRNA in SMCs (A) is shown. After SMCs were transfected with eEF2K siRNA or control siRNA (40 nmol/l, 24 h), total cell lysates were harvested. Expression of eEF2K protein (n = 3) was determined by Western blotting and shown as fold change relative to control siRNA. Equal protein loading was confirmed using total-α-actin antibody. **P < 0.01 vs. control siRNA. Effects of eEF2K knockdown on TNF-α-induced VCAM-1 expression (B) are also shown. After SMCs were transfected with eEF2K siRNA or control siRNA, they were treated with 10 ng/ml TNF-α for 24 h. VCAM-1 expression was determined by Western blotting and shown as fold increase relative to control siRNA without TNF-α stimulation. Equal protein loading was confirmed using α-actin antibody. Effects of eEF2K knockdown on TNF-α-induced phosphorylation of JNK (C) and NF-κB p65 (Ser536) (D) are also shown. After transfection with eEF2K siRNA or control siRNA (40 nmol/l, 24 h), SMCs were stimulated with 10 ng/ml TNF-α for 20 min. Phosphorylation of JNK (n = 6) and NF-κB (n = 4) was determined by Western blotting and shown as fold increase relative to control siRNA without TNF-α stimulation. Equal protein loading was confirmed using total antibody. **P < 0.01 vs. control siRNA without TNF-α; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. cont siRNA + TNF-α.
