Fig. 4.
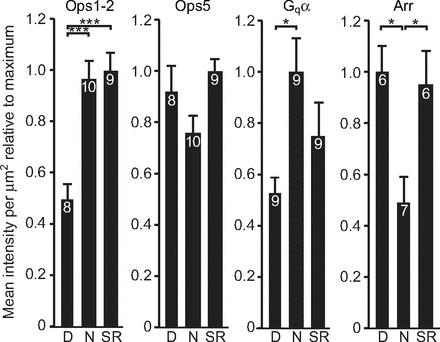
RhOps1-2, RhGqα and RhArr levels change significantly day to night while levels of RhOps5 levels do not. Quantification of average Ops1-2-, Ops5-, Gqα- and Arr-ir per μm2 of rhabdoms in LEs from animals maintained in natural illumination. Eyes were fixed during the day (D) between 7 and 10 h after sunrise, during the night (N) between 4 and 6 h after sunset, or at sunrise (SR). The mean immunoreactivity per μm2 of rhabdom in individual ommatidia was determined as described in the Materials and methods and in the legend to Fig. 2. Data from eight different ommatidia in an eye were averaged to determine the mean intensity for that eye. Data for each antigen were pooled from three to four confocal sessions each involving eyes from two to four different animals at each time point; the numbers in each bar show the total number of animals assayed. Data are expressed as mean (±s.e.m.) immunoreactive intensities per μm2 of rhabdom relative to the mean maximum immunoreactive intensity per μm2. The significance of differences among time points was tested with a one-way ANOVA followed by the Student–Newman–Keuls test (***P<0.001, *P<0.05). Data for Ops1-2 and Ops5 are adapted from Katti et al. (Katti et al., 2010).
