Fig. 6.
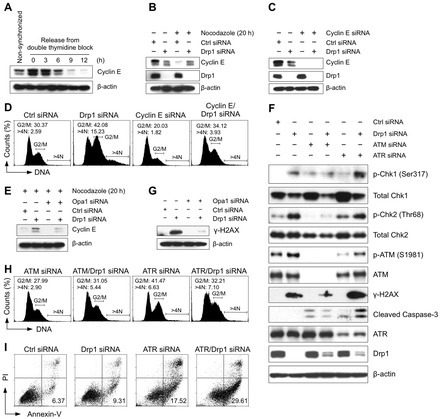
The G2/M cell cycle arrest and aneuploidy observed in Drp1-deficient cells result from replication stress-initiated DNA damage signaling that involves ATM/Chk2 and ATR/Chk1 kinases. (A) Cyclin E expression during the cell cycle. MDA-MB-231 cells were synchronized at G1/S border by a double thymidine block and then released in fresh media containing nocodazole. Cells were then harvested at the indicated time points, and the expression of cyclin E was detected by western blot. (B) Loss of Drp1 causes an accumulation of cyclin E in the G2/M phase. Cyclin E expression was assessed by western blot by using cell extracts generated from the control cells and from Drp1-deficient cells in the presence or absence of nocodazole for 20 h. (C) Knockdown efficiency of cyclin E and Drp1 was confirmed by western blot. (D) The loss of cyclin E reverses the G2/M cell cycle arrest and aneuploidy observed in Drp1-deficient cells. Four days after siRNA transfection, cell cycle distribution was determined by flow cytometric analysis of propidium iodide stained cells. The percentage of cells containing a DNA content of 4N and DNA content greater than 4N is indicated. (E) Loss of Opa1 reverses cyclin E accumulation in G2/M phase observed in Drp1-deficient cells. (F) Loss of Drp1 induces a DNA damage response. Cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA for four days and the changes in the proteins associated with the DNA damage response were assessed by western blot. (G) Loss of Opa1 prevented the accumulation of γ-H2AX in Drp1-deficient cells. (H) Loss of ATM reverses the G2/M cell cycle arrest and aneuploidy observed in Drp1-deficient cells, whereas the loss of ATR induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and aneuploidy. Four days after siRNA transfection, the cell cycle distribution was determined, as previously described. (I) ATR is essential for the survival of Drp1-deficient cells. Cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA for four days and apoptosis was assessed by annexin V and PI staining. The percentage of annexin V-positive and PI-negative early apoptotic cells is indicated. These data represent three independent experiments.
