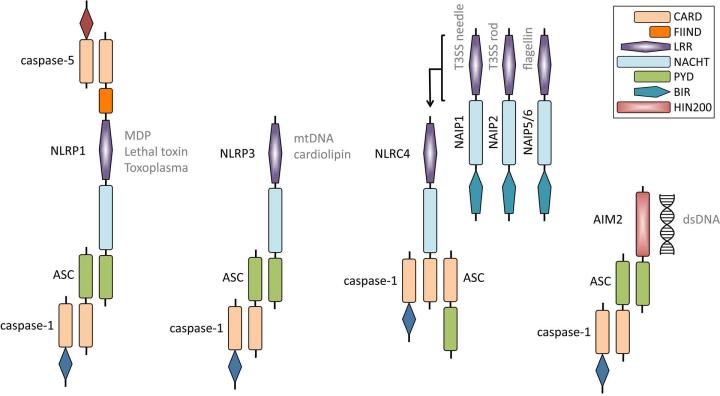
Figure 1.
Schematic of NLRP1, NLRP3, NLRC4, and AIM2 inflammasomes. Human NLRP1 can interact with ASC and caspase-1 via an N-terminal PYD and also bind caspase-5 to the complex via the C-terminal CARD. Muramyl dipeptide (MDP), Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin, and Toxoplasma gondii can induce the activation of the NLRP1 inflammasome. Mouse Nlrp1b does not possess a functional N-terminal PYD, hence caspase-1 may interact with its C-terminal CARD. NLRP3 interacts with ASC through an N-terminal PYD domain, which then recruits caspase-1. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and cardiolipin have been postulated to bind to NLRP3 and induce its activation. The NLRC4 inflammasome is activated by the intermediary molecules NAIP1, NAIP2, and NAIP5/6, which have been shown to bind to the type three secretion system (T3SS) needle and rod proteins and bacterial flagellin, respectively. It remains unclear how ASC interacts with the NLRC4 inflammasome complex. The AIM2 inflammasome can directly bind double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) via its HIN200 domain. AIM2 recruits ASC and caspase-1 through its N-terminal PYD domain. CARD, caspase recruitment domain; FIIND, domain with function to find; NACHT, nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain; PYD, pyrin domain; LRR, leucine-rich repeats; BIR, baculovirus IAP repeat domain; HIN200; HIN-200 domain.