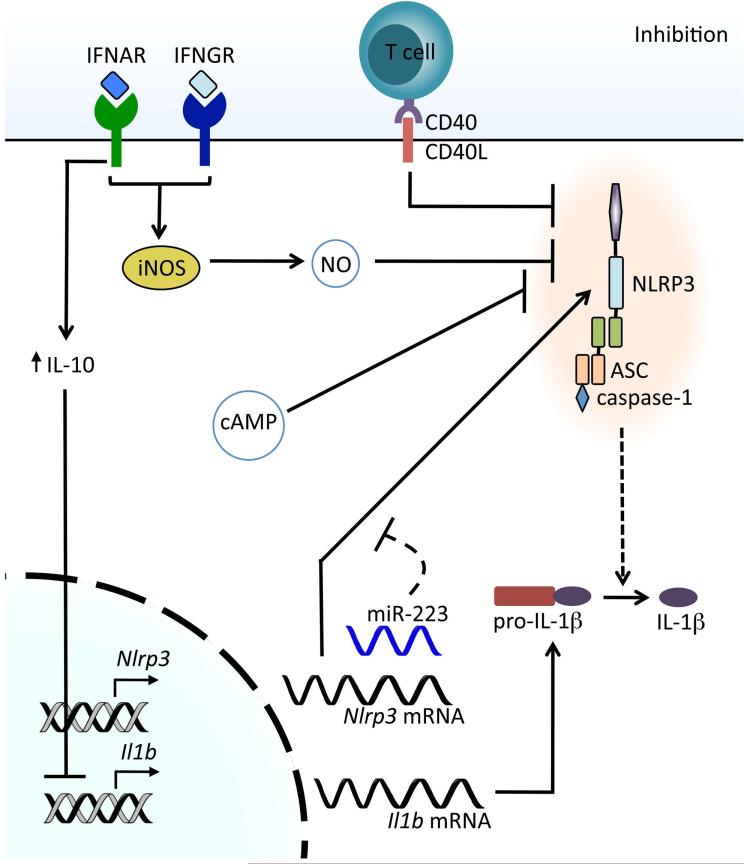
Figure 3.
Inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Type I IFNs acting through IFNAR inhibit the transcription of pro-IL-1β through the upregulation of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. Type I IFNs and IFN-γ inhibit NLRP3 through the production of nitric oxide (NO) via the inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), resulting in nitrosylation of NLRP3. Interaction of mature or memory T cells with macrophages via CD40–CD40L results in inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Elevation of cellular cAMP levels also results in the inhibition of NLRP3. The microRNA mir-223 regulates the amount of NLRP3 mRNA and, consequently, NLRP3 expression.