Fig. 1.
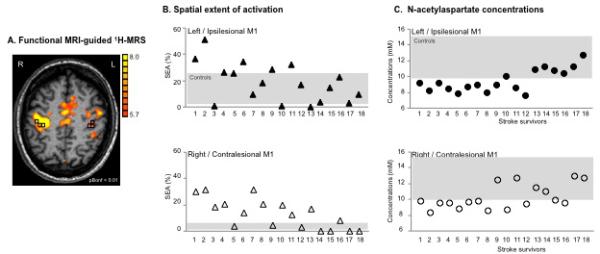
(A) Motor-related cortical activation during a handgrip task executed with the impaired right hand in a 45-age old patient who had experienced infarct involving the left basal ganglia and corona radiata (Patient 7, Table 1). Spectroscopic voxels (black squares) were selected in the hand knob area (based on M1 activation and/or anatomical landmarks in case the activation tended to zero). The front of the brain is upwards. L=left, R=right. (B) Spatial extent of M1 activation during handgrip executed with the impaired hand (%) and (C) NAA concentrations (mM) in both ipsilesional (upper row, closed symbols) and contralesional (lower row, open symbols) M1 are shown for individual patient. Stroke survivors are ranked by FMUE scores (see Table 1, with #1, no arm motor impairment; #18, severely impaired). Grey rectangles signify the range of spatial extent activation (B) and NAA concentrations (C) in left (upper row) and right (lower row) M1 in healthy controls.
