Fig. 1.
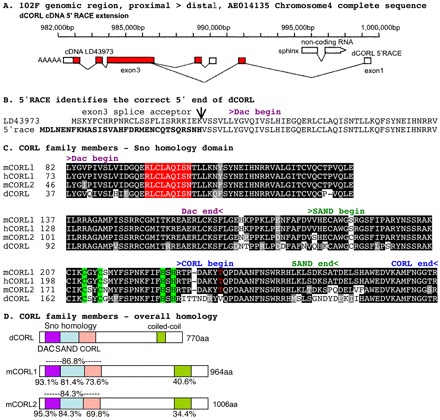
The Drosophila CORL locus, 5′RACE and alignments. (A) The CORL cDNA LD43973 and its extension by 5′RACE with exons shown as boxes (white, untranslated; red, protein coding). CORL transcription direction is shown by a poly-A tail and sphinx transcription direction (opposite from CORL) is indicated by an arrowhead. The CORL proximal start site at 990,000 bp corresponds to the 5′ end of LD43973 and the CORL start site identified by 5′RACE at 986,265 bp is distal to sphinx. The 5′RACE product is consistent with the prediction for CG11093 isoform B (GenBank Accession Number ACZ95098). (B) The open reading frames contained within exon 2 of both transcripts (5′RACE in bold) and their splice junctions with the common exon 3 are shown. (C) Sno homology domain of CORL aligned with mouse Corl1, mouse Corl2 and human CORL1. An amino acid is shaded if the residue is identical (black) or similar (gray), with coloring indicating the APC recognition site (red) and Cys2-His2 zinc finger (green). The red T (mCorl1 Thr235) absent in CORL is homologous to Smad4-binding Thr271 in human Ski. Conserved motifs within the Sno homology domain are Dac, SAND and CORL. (D) CORL proteins from fly and mouse with the locations of five distinct domains shown. The level of amino acid similarity between the indicated protein and Drosophila CORL is shown for all five domains.
