Fig. 6.
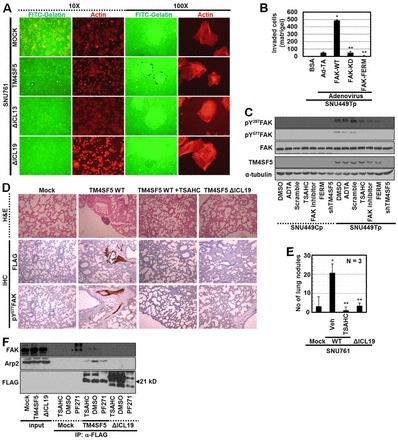
ΔICL19 mutation blocks FAK activity and invasion and metastasis. (A) SNU761 cells stably expressing FLAG-TM4SF5 WT, ΔICL13, or ΔICL19 mutants were cultured on coverglasses precoated with Oregon Green® 488-conjugated gelatin for 24 h. Immunofluorescent microscopic visualization to see degradation of the gelatin and actin were performed. (B) SNU449Tp cells infected with control and diverse adenovirus for FAK forms for 24 h were analyzed for matrigel invasion for 24 h. Invaded cells were stained, imaged and counted for the mean ± standard deviation. (C) Subconfluent cells were treated with diverse reagents or infected with (HA)3-FAK FERM adenovirus or transfected with shRNA against TM4SF5 (shTM4SF5) for 24 h, before harvests and standard western blotting for the indicated molecules. (D) H&E staining or immunohistochemistry of lung tissues using anti-FLAG or pY577FAK antibodies were performed using slices of lung tissue from mice tail-vein-injected with SNU761 cells stably expressing mock, TM4SF5 WT, or ΔICL19 mutant. Mice injected with SNU761-TM4SF5 WT cells were treated with DMSO or TSAHC every other day. (E) Number of nodules on lungs from mice (as in D) to indicate in vivo lung metastasis of TM4SF5 WT (but not ΔICL19 mutant)-expressing SNU761 cells via tail vein injection, depending on TSAHC administration. * P≤0.05 against control virus (Ad-TA; B) or mock (E); **P≤0.05 against FAK WT (B) or TM4SF5 WT (E) cells. (F) Stable SNU761 cells (expressing FLAG-mock, -TM4SF5 WT or -ΔICL19 mutant) were prepared after treatment of DMSO, TSAHC, or FAK inhibitor (PF271) for 24 h. Whole extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody, before standard western blotting for the molecules. *Depicts unknown coimmunoprecipitates (at different molecular weights) from FAK inhibitor-treated mock cells. Data represent three independent experiments.
