Fig. 2.
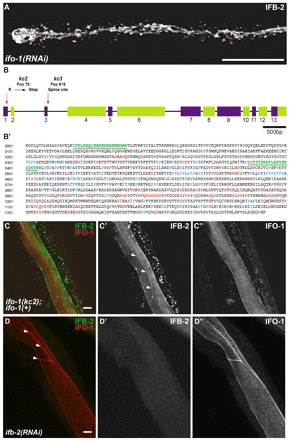
kc2 and kc3 are alleles of gene F42C5.10 encoding intestinal filament organizer IFO-1, which colocalizes with IFB-2. (A) Fluorescence image of IFB-2::CFP-expressing reporter strain BJ52 after RNAi against F42C5.10-encoded RNA shows identical phenotype to kc2 mutant (see Fig. 1C,D). (B,B′) Structure of the F42C5.10 ifo-1 gene and encoded polypeptide sequence. The 5789 bp-long gene consists of 13 exons. Mutant allele kc2 carries a C→T mutation at position 79 leading to a stop codon in the first exon, kc3 a G→A mutation at position 919, which is the first position of the 5′ donor splice site of the third intron. The encoded polypeptide, referred to as IFO-1, is 1292 amino acids long. It is rich in histidines (marked in red) and contains a proline-rich region (prolines highlighted in blue). The two peptides (green) used for antibody generation are underlined. (C-C″) Fluorescence microscopy of mutant kc2 worms of strain BJ133 that were microinjected with an ifo-1::yfp rescue construct. The normal-appearing, fully rescued IFB-2::CFP fluorescence in green (false color) co-distributes with the IFO-1::YFP fluorescence (false red color). (D-D″) Fluorescence microscopy of isolated WT intestines after ifb-2(RNAi) that were stained against IFB-2 (false green color) and with purified anti-IFO-1 peptide antibodies (false red color; peptide 2 in B′). Arrows in C′ and D delineate the CeAJ. Scale bars: 50 μm in A; 10 μm in C,D.
