Fig. 4.
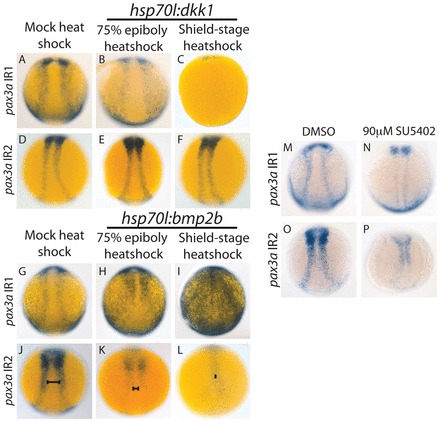
pax3a IR1 requires Wnt and FGF signaling, and pax3a IR2 requires BMP and FGF signaling for full activity. (A-F) dkk1 was overexpressed by heat shock in embryos with pax3a IR1:GFP or pax3a IR2:GFP. pax3a IR1 activity decreased with dkk1 overexpression induced with a 75% epiboly heatshock (100%, n=25) (B versus A) and was almost completely lost with a shield stage heat shock (100%, n=12) (C versus A). pax3a IR2:GFP activity did not decrease when dkk1-mCherry overexpression was induced by heat shock at 75% epiboly (92%, n=12) (E versus D) or shield stage (89%, n=18) (F versus D). (G-L) bmp2b was overexpressed by heat shock. pax3a IR1activity intensifies and expands into the neural plate and epidermis when bmp2b overexpression is induced with a 75% epiboly heat shock (93%, n=41) (H versus G) and heat shock at shield stage leads to an even greater activity increase and causes expansion into the entire neural plate (84%, n=19) (I versus G). pax3a IR2 activity decreases and shifts medially (J-L, bars) upon bmp2b induction by 75% epiboly heat shock (100%, n=33) (K versus J) and further decreases and shifts medially into a tear-drop shape with a shield-stage heat shock (100%, n=14) (L versus J). (M-P) SU5402 treatment (90 μM) beginning at 7 hpf causes a decrease in the activity of pax3a IR1 (94%, n=17) (N versus M) and pax3a IR2 (100%, n=25) (P versus O). All pictures are dorsal trunk views with anterior upwards.
