Fig. 9.
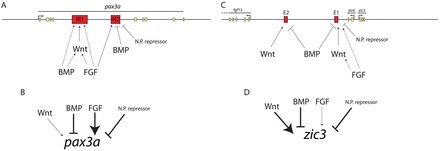
pax3a and zic3 are regulated by integrating inputs from multiple enhancers and signaling pathways. (A) pax3a IR1 requires Wnt and FGF signaling for its full activity and is activated by BMP signaling. The effect of Wnt signaling is probably direct. FGF and BMP signaling could be acting directly on IR1 or indirectly through Wnts (broken lines) as Wnt ligands are upregulated upon bmp2b overexpression (supplementary material Fig. S3) and Wnts are upregulated upon FGF overexpression in Xenopus (Hong et al., 2008). pax3a IR2 is repressed by BMP overexpression, requires FGF signaling for full activity and is probably repressed by a neural plate factor (N.P. repressor). (B) NPB pax3a expression has a strong requirement for FGF signaling and a weaker requirement for Wnt signaling. pax3a expression is repressed by BMP overexpression and probably by a repressor in the neural plate. (C) zic3 E1 requires FGF and Wnt signaling for full activity and is repressed by BMPs. FGF could be acting indirectly by inducing expression of Wnt ligands. zic3 E2 requires Wnt signaling for NPB activity and is repressed by BMP overexpression. (D) zic3 NPB expression has a strong requirement for Wnt signaling and a cryptic requirement for FGF signals that only becomes apparent when Wnt signaling is attenuated. zic3 in the NPB is repressed by BMP overexpression and probably also repressed by a factor in the neural plate.
