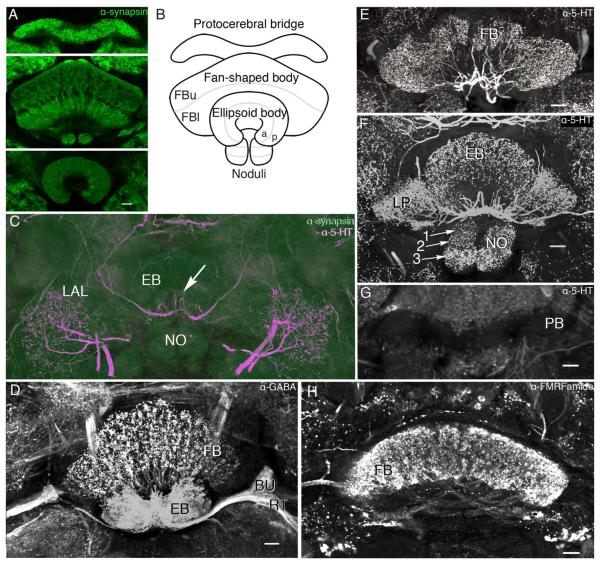
Figure 2.
Organization of the central complex of Neobellieria bullata. A: Antisynapsin staining of the protocerebral bridge, fan-shaped body (FB), noduli (NO), and ellipsoid body (EB). B: Schematic of central complex structures viewed frontally (ventral according to the neuraxis) showing the division of the fan-shaped body into upper (FBu) and lower (FBl) divisions, the EB into anterior (a) and posterior (p) rings, and the NO into three layers. C: Antisynapsin (green) and antiserotonin (5-HT; magenta) staining of an oblique section through the NO, EB, and lateral accessory lobes (LAL) showing three compartments of the NO (I, II, III), and the EB divided into two rings, anterior (a) and posterior (p), based on antisynapsin staining. Labeling with antisynapsin and anti-5-HT reveals a network of serotonin-like immunoreactive arbors innervating the LAL and two axons entering the EB, where they provide radiating branches (arrow). D: Oblique frontal section showing dense γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-like immunoreactivity in the EB, bulbs (BU), and ring neuron tract (RT) as well as a layer of anti-GABA immunoreactivity in the FB. E: Oblique frontal section through the FB showing processes of neurons labeled with anti-5-HT arborizing within modules of the FB. F: Frontal section through the EB, NO, and lateral protuberances (LP) of the FB show extensive serotonin-like immunoreactivity. The noduli are shown divided into three discrete zones (arrows 1–3). G: Frontal section through the protocerebral bridge showing it devoid of serotoninergic innervation. H: Horizontal section through the FB showing dense FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity in all modules and the fibers that interconnect them. Scale bars = 20 μm. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]