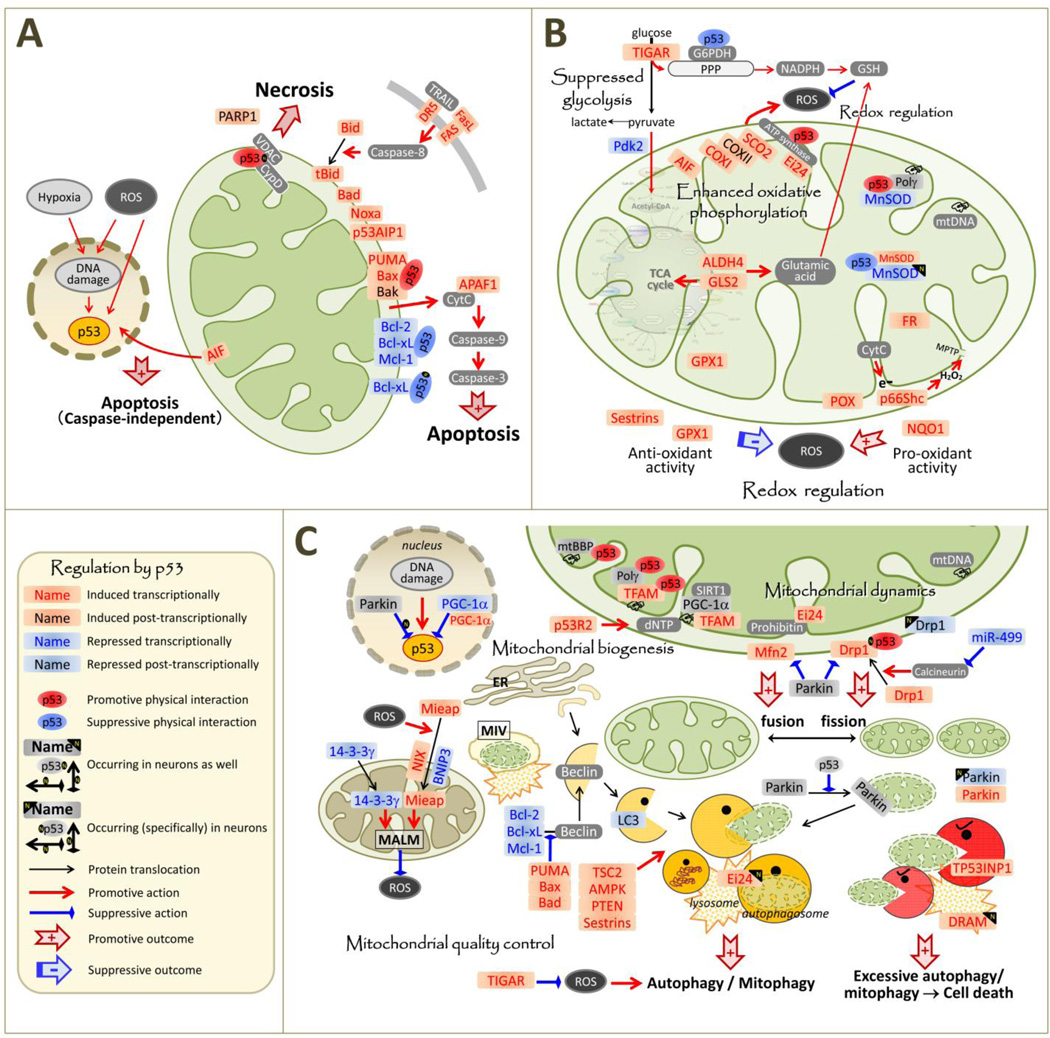
Figure 2.
p53-regulated proteins and their interacting proteins and pathways in relation to mitochondrial function. Note that p53-mediated regulation of gene expression is most likely cell and stress type-specific and the proteins listed as “induced/repressed by p53” may not be regulated that way in neurons. Proteins are listed as “transcriptionally induced/repressed by p53” only when the transcriptional regulation has been demonstrated at the gene structure level (promoter reporter assay, CHIP analysis). Not all proteins/genes mentioned in the text are presented in these figures. Note that essentially all the apoptosis-related proteins shown in (A) are transcriptionally regulated in similar ways in neurons at least under certain specific apoptotic conditions, but this is not reflected in the figure for the purpose of simplicity. Abbreviations: AIF: apoptosis-inducing factor, mitochondrion-associated, 1; ALDH4; aldehyde dehydrogenase 4 family, member A1: AMPK: 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; APAF1: Apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1; Bad: Bcl-2-associated death promoter; Bak: Bcl-2-homologous antagonist/killer; Bax: Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma 2; Bcl-xL: B-cell lymphoma-extra-large (BCL2-like 1); Bid/tBid: (truncated) BH3 interacting domain death agonist; BNIP3: BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3; COX: cytochrome c oxidase; CypD: cyclophilin D; CytC: cytochrome c; dNTPs: deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates; DR5: tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10b; DRAM: DNA damage-regulated autophagy modulator protein; Drp1: dynamin-related protein 1; Ei24: Etoposide-induced protein 2.4 homolog (PIG8); ER: endoplasmic reticulum; FAS: Fas cell surface death receptor; FASL: FAS ligand; FR: ferredoxin reductase; G6PDH: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; GLS2: Phosphate-activated mitochondrial glutaminase; GPX1: glutathione peroxidase 1; GSH: reduced glutathione; LC3: microtubule-associated protein light chain 3; MALM: Mieap-induced accumulation of lysosome-like organelles within mitochondria; Mcl-1: myeloid cell leukemia-1; Mfn2: mitofusin 2; Mieap: mitochondria eating protein; MIV: Mieap-induced vacuole; MnSOD: manganese superoxide dismutase; MPTP: mitochondrial permeability transition pore; mtSSB; mitochondrial single-stranded DNA-binding protein: mtDNA: mitochondrial DNA; Nix: NIP-like protein X (a.k.a., BNIP3-like protein); Noxa: phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1 (PMAIP1); NQO1: quinone oxidoreductase or NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1; p53: tumor protein 53; p53AIP1: tumor protein p53 regulated apoptosis inducing protein 1; p53R2: ribonucleotide reductase M2 B (RRM2B); p66Shc: p66 isoform of Src homology 2 domain-containing-transforming protein C1; PARP1: poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; Pdk2: Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase isoform 2; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha; POX: proline oxidase 1; PPP: pentose phosphate pathway; Polγ: DNA polymerase subunit gamma; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; PUMA: p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis; ROS: reactive oxygen species; SCO2: cytochrome c oxidase assembly; SIRT1: sirtuin 1; TSC2: Tuberous sclerosis protein 2; TFAM: mitochondrial transcription factor A; TIGAR: TP53-inducible glycolysis and apoptosis regulator; TP53AIP1: tumor protein p53 regulated apoptosis inducing protein 1; p53INP1: VDAC: voltage-dependent anion channel.