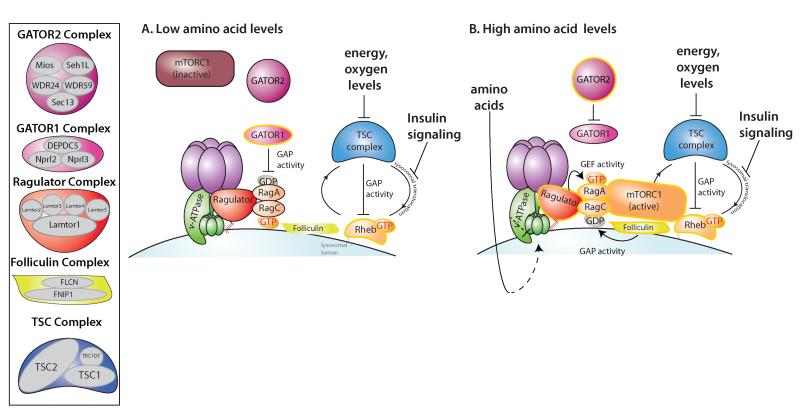
Figure 1. The mTORC1 amino acid sensing pathway.
A. Under low amino acid conditions Ragulator is found in an inhibitory state with the v-ATPase and GATOR1 exerts its GAP activity towards RagA, keeping this GTPase in the inactive GDP-bound state that is not sufficient to recruit mTORC1. Insulin signaling inhibits TSC complex translocation to the lysosomal surface where it functions as a GAP for Rheb, inactivating this G protein. B. Upon amino acid stimulation, GATOR1 may be inhibited by GATOR2 and Ragulator and v-ATPase undergo a conformational change unleashing the GEF activity of Ragulator towards RagA, while the folliculin complex promotes RagC GTP hydrolysis. The now active heterodimer, consisting of GTP-bound RagA and GDP-loaded RagC, recruits mTORC1 to the lysosomal surface, where it interacts with and is activated by Rheb.