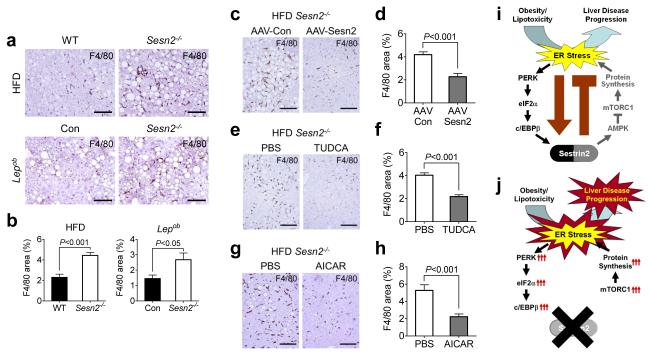
Figure 6. Sestrin2 is an endogenous attenuator of steatohepatitis progression.
(a-b) Livers from WT and Sesn2−/− mice kept on HFD (HFD panels) or Lepob/ob/Sesn2+/− (Con) and Lepob/ob/Sesn2−/− mice kept on LFD (Lepob panels) were subjected to anti-F4/80 staining to visualize macrophage infiltration (a). F4/80-positive areas were quantified (b). (c-h) Livers from obese Sesn2−/− mice transduced with AAV-Con (n = 4) or AAV-Sesn2 (n = 3) (c,d) or injected with PBS (n = 4) or TUDCA (n = 5) (e,f) or PBS (n = 6) or AICAR (n = 5) (g,h) were analyzed by anti-F4/80 staining (c,e,g). F4/80-positive areas were quantified (d,f,h). Nuclei were visualized by hematoxylin (a,c,e,g). (i,j) Working model of how Sestrin2-mediated UPR attenuates NAFLD progression. In WT liver, Sestrin2 is induced during obesity through the PERK-c/EBPβ pathway to attenuate protein translation and thereby relieve ER stress (i). In Sesn2−/− liver, persistent mTORC1 activity elevates protein synthesis and subsequently aggravates ER stress, leading to facilitated NAFLD progression (j). Scale bars, 200 μm. All data are shown as the mean ± s.e.m. P values are from Student’s t test.