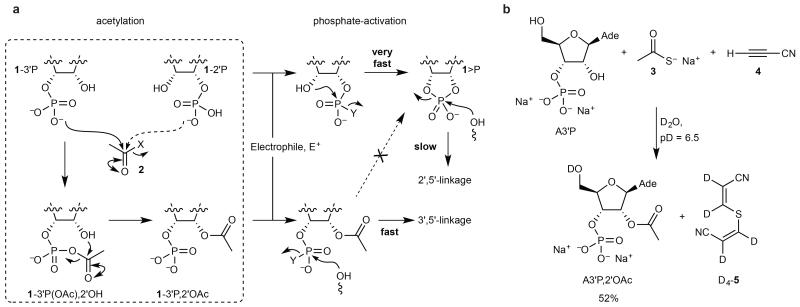
Figure 1. Chemoselective acetylation of RNA.
a, Protection of the 2′-OH group of 1-3′P facilitates rapid template-directed 3′,5′-ligation following electrophilic phosphate activation. The 3′-OH group of 1-2′P is protected to a lesser extent such that 1>P is the major product of phosphate activation and slow template-directed 2′,5′-ligation follows. b, Treatment of adenosine-3′-phosphate (A3′P, 100 mM) with sodium thioacetate 3 (100 mM) and cyanoacetylene 4 (200mM) in D2O at neutral pD for 24 h results in selective acetylation of the 2′-OH group. Curly arrows indicate electrophilic activation/acetylation steps. X, leaving group; Y, leaving group generated by electrophilic activation of phosphate oxygen, with or without a subsequent nucleophilic displacement; Ade, N9-linked adenine; yield judged by 1H-NMR integration.