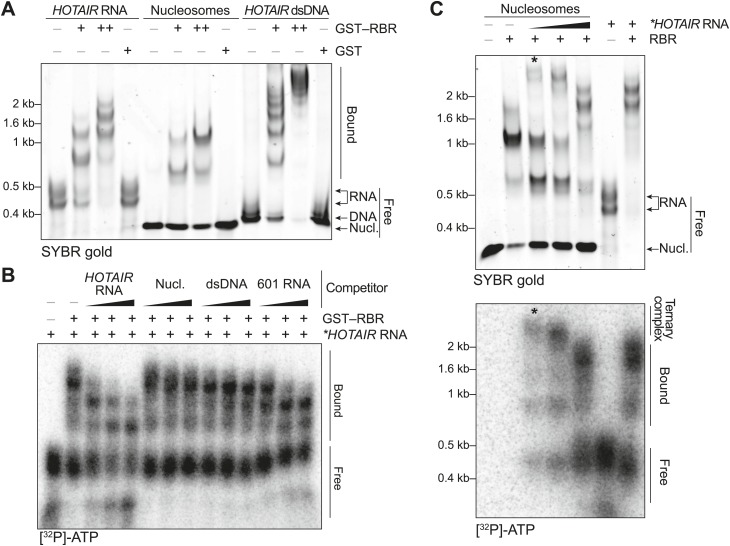
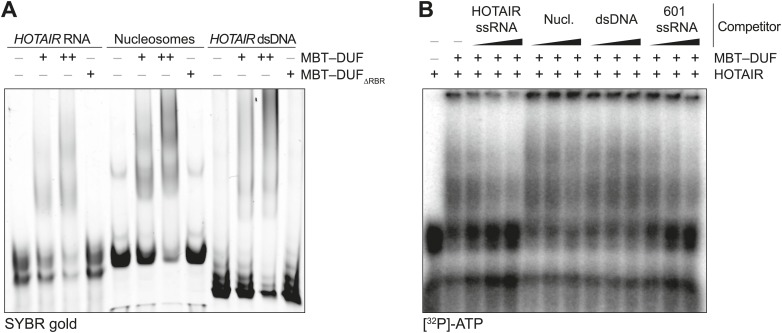
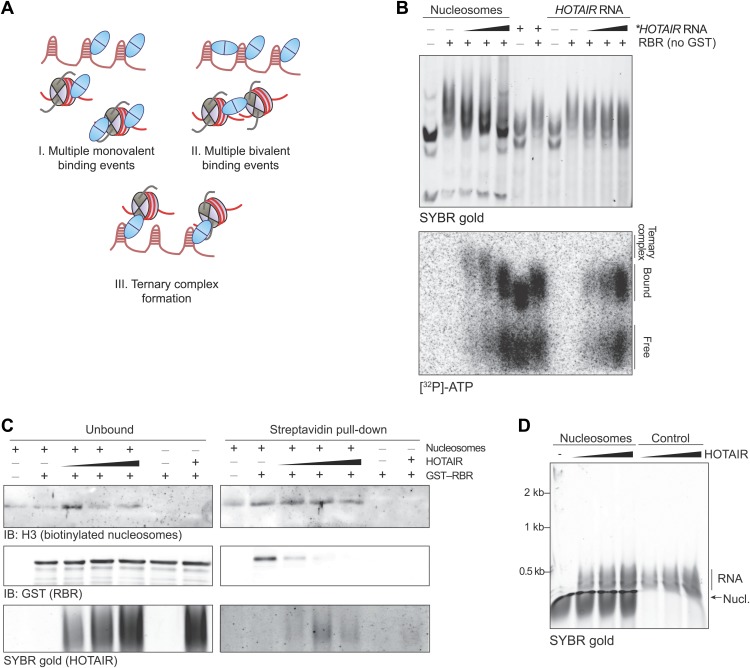
Figure 2. In vitro characterization of the binding preferences of the SCML2 RBR.
(A) EMSA with 2 (+) and 4 (++) pmol GST-fused RBR and 520 fmol HOTAIR RNA 1–300, 690 fmol nucleosomes, or 275 fmol dsDNA encoding HOTAIR1–300. 5.2 pmol GST were used as a control. Complexes were separated on native gels and detected with SYBR gold stain. Data are representative of ≥4 experiments. (B) EMSA with 3.4 pmol GST–RBR and 520 fmol of labeled HOTAIR RNA was performed as in (A) with the addition of, from left to right, 260, 520, and 1040 fmol of unlabeled HOTAIR RNA, nucleosome particles, dsDNA, and 601 RNA. Bands were visualized by autoradiography. Data are representative of ≥4 experiments. (C) EMSA of RBR with nucleosomes and labeled HOTAIR RNA. Assay was performed as in (B) varying the amount of labeled RNA. Nucleic acid stain (top) and autoradiography (bottom) are shown. The asterisk indicates the putative ternary complex.