Figure 3.
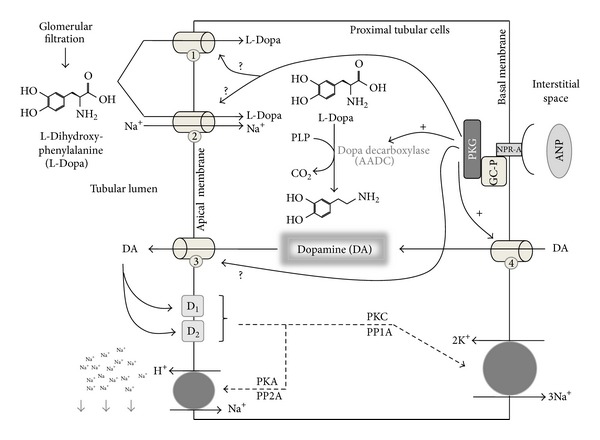
The synthesis and tubular handling of dopamine. Filtered L-Dopa can be uptaken by two different mechanisms: (1) sodium independent transporters (LATs) and (2) sodium dependent transporters (system B0). L-Dopa is rapidly decarboxylated to dopamine (DA) by Dopa decarboxylase enzyme, using pyridoxal 5-phosphate hydrate (PLP) as cofactor. Dopa decarboxylase activity can be regulated by different hormones, like angiotensin II or atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), among others. Newly formed dopamine can leave the cells through the apical border (3), probably mediated by organic cationic transporters (OCTNs). Circulating dopamine can enter into proximal tubular cells through basal located OCTs (4). Full arrows and “+”: stimulating action of PKG; full arrows and question mark “?” suggest a possible regulatory mechanism; dashed arrows suggest the intracellular signaling.
