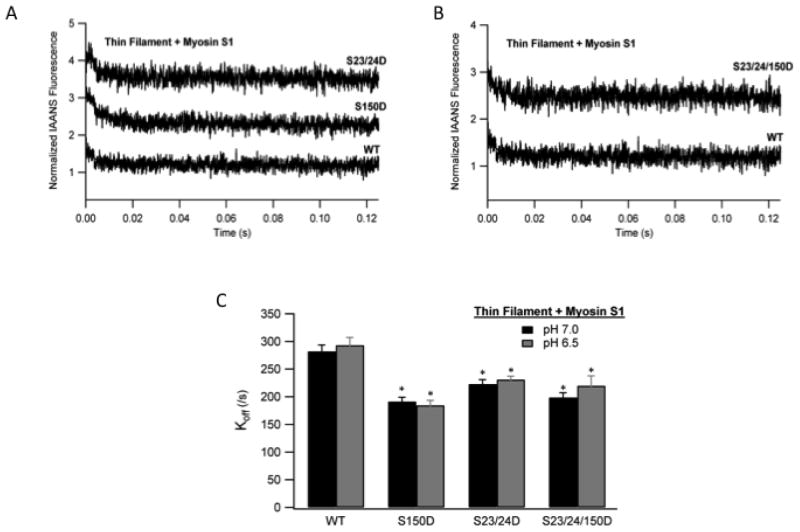
Fig. 5. The effect of TnI phosphorylation on Myosin S1 dissociation kinetics from thin filaments at ischemic pH.
Ca2+ free thin filaments containing rigor bound myosin S1 were rapidly mixed with ATP and the dissociation of myosin S1 monitored as the change in IAANS TnC fluorescence. Representative stopped-flow traces from myosin S1 bound thin filaments containing WT TnI (WT) vs. pseudo-phosphorylated TnI Ser-150 (S150D) and pseudo-phosphorylated TnI Ser-23/24 (S23/24D) filaments (A) or pseudo-phosphorylated TnI Ser-23/24/150D (S23/24/150D) filaments (B). Traces demonstrating the change in fluorescence over time are normalized and staggered for clarity. Comparison of the myosin S1 dissociation rates (koff) from WT, S150D, S23/24D, and S23/24/150D containing thin filaments at pH 7.0 (black) and pH 6.5 (dark gray). (C). *P<0.05 vs. WT.