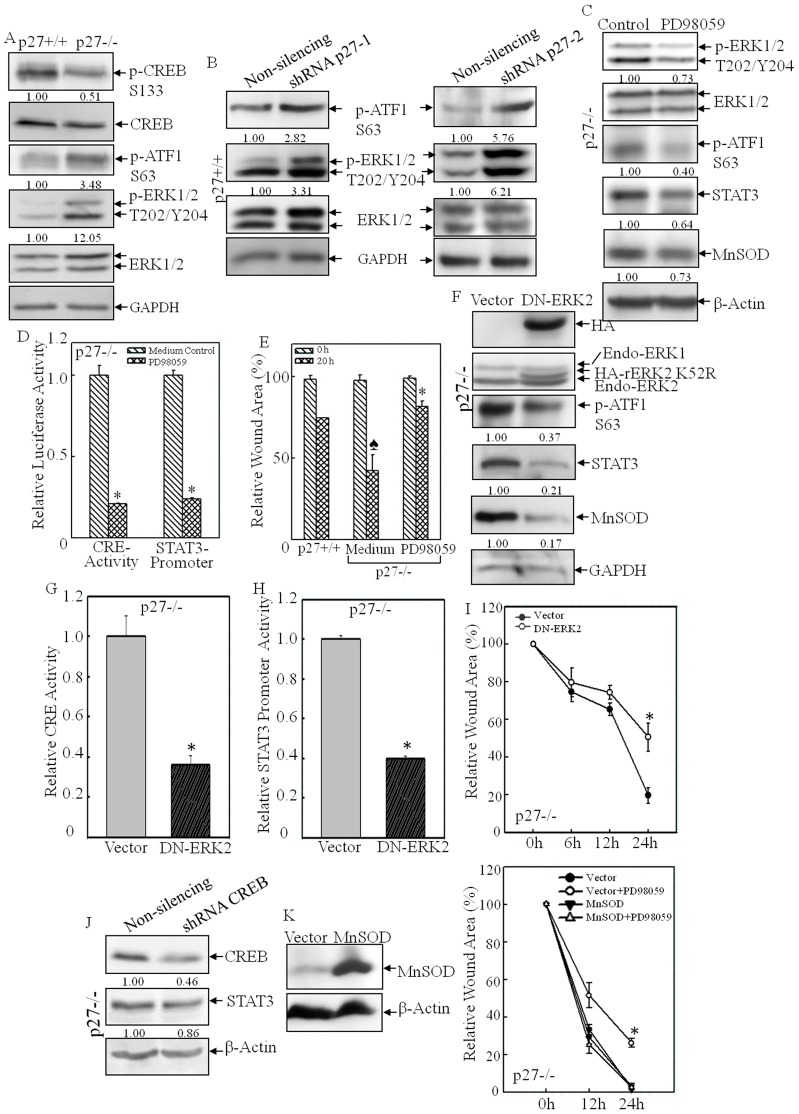
Fig. 8.
CRE transactivation was mediated by the ERK–ATF1 pathway in p27−/− MEFs. (A,B) The levels of phosphorylated forms of ERK, CREB and ATF1 were assessed by western blotting in p27+/+ and p27−/− MEFs (A) and shRNA-p27 and non-silencing control transfectants (B). (C–E) PD98059 treatment efficiently blocked ERK–ATF1–CRE activation (C,D), STAT3 and MnSOD expression (C,D) and cell migration in p27−/− MEFs (E). *P<0.05 (between PD98059 treatment and medium control); P<0.05 (between p27+/+ and p27−/− MEFs). (F–I) DN-ERK2 stable transfectants were identified by western blotting (F). Ectopic expression of DN-ERK2 impaired ATF1–CRE activation (F,G), Stat3 transcription (H), Stat3 protein expression (F) and cell migration in p27−/− MEFs (I). *P<0.05 (between DN-ERK2 and vector-control transfectants). (J) Knockdown of CREB did not affect STAT3 expression. (K) MnSOD was overexpressed in p27−/− MEFs and the cell migration was assessed by using the wound-healing assay in the presence or absence of the ERK inhibitor PD98059. For panels A–C,F,J, densitometric quantification is shown beneath the blots.