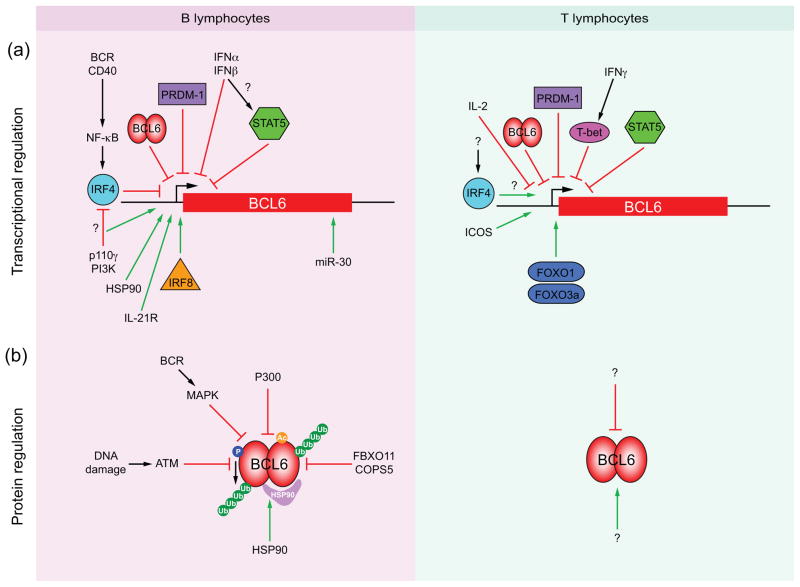
Figure 2.
Molecular mechanisms of BCL6 regulation in B and T lymphocytes. (a) Transcriptional regulators of BCL6 induction (green arrows) and down-regulation (red bars) in B and T lymphocytes. Transcription factors, of which IRF4, IRF8, STAT5, T-bet and Foxo1 and Foxo3a bind directly to the BCL6 gene control region, are indicated by colored shapes. Question marks signify unknown mediators and putative effects. (b) Post-translational regulation of BCL6 protein stabilization (green arrows) and degradation (red bars) in B and T lymphocytes. Acetylation (Ac) of BCL6 by P300 mediates BCL6 protein degradation. Phosphorylation (P) of BCL6 by MAPK or ATM results in BCL6 ubiquitylation (Ub) and proteasome-mediated degradation. FBXO11 and COPS5 also mediate ubiquitin-dependent degradation of BCL6. The HSP90 chaperone stabilizes the BCL6 protein half-life. Question marks signify unknown mediators of BCL6 protein stabilization and degradation in T-cells.