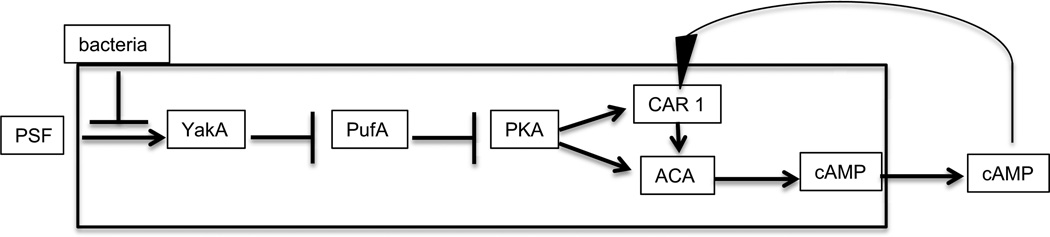
Figure 3.
The growth- differentiation transition pathway. Growing amoebae secrete PSF continuously such that the concentration increases as the cell density increases. When it reaches threshold, it activates the protein kinase YakA. If bacteria are still around, the threshold is higher. YakA activity inhibits PufA which inhibits translation of the catalytic subunit of PKA. Inhibiting an inhibitor results in activation of PKA. This cAMP dependent protein kinase leads to the accumulation of the cAMP receptor CAR1 and the adenylyl cyclase ACA which synthesizes cAMP. Most of the newly made cAMP is secreted into the surrounding fluid where it can diffuses to bind to the receptor on the same cell (autocrine) or other cells (paracrine). Ligand binding to CAR1 stimulates ACA thereby forming a positive feedback loop.